Abstract
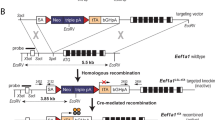
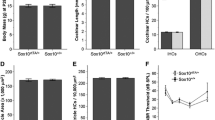
Transgenic mouse models mediating conditional temporal and spatial regulation of gene expression to the respiratory epithelium were developed utilizing the reverse tetracycline transactivator (rtTA) expressed under the control of SP-C and CCSP promoters. Luciferase activity was detected in the lungs of fetal and adult double transgenic mice but was not detected in other tissues or in single transgenic mice. In adult mice, maximal luciferase activity was detected 16 h after the administration of doxycycline in the drinking water, or 2 h after the injection of doxycycline. Activation of the transgene was observed after the administration of doxycycline in food pellets. After prolonged exposure to doxycycline, luciferase activity decreased slowly following removal of doxycycline, suggesting the importance of tissue pools which maintained expression of the transgene. In SP-C-rtTA mice, exposure of the pregnant dam to doxycycline induced luciferase activity in fetal lung tissue as early as E10.5. Luciferase activity was maintained in the lung tissue of pups during the period of lactation when the mother received doxycycline in the drinking water. In the CCSP-rtTA mice, luciferase was not detected in the absence of doxycycline. In the SP-C-rtTA mice, luciferase activity was detected in the absence of doxycycline but was enhanced approximately 10-fold by administration of drugs. The SP-C-rtTA and CCSP-rtTA activator mice control the expression of transgenes in the developing and mature respiratory epithelium, and will be useful for the study of gene function in the lung.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albanese C, Reutens AT, Bouzahzah B, Fu M, DAmico M, Link T, Nicholson R, Depinho RA and Pestell RG (2000) Sustained mammary gland-directed, ponasterone A-inducible expression in transgenic mice. FAS EB J 14: 877–884.
Danielian PS, Muccino D, Rowitch DH, Michael SK and MacMahon AP (1998) Modification of gene activity in mouse embryos in utero by a tamoxifen-inducible form of Cre recombinase. Curr Biol 18: 1323–1326.
Glasser SW, Burhans MS, Eszterhas SK, Bruno MD, Korfhagen TR (2000) Human SP-C gene sequences that confer lung epithelium-specific expresssion in transgenic mice. Am J Physiol 278: L933–L945.
Glasser SW, Korfhagen TR, Bruno MD, Dey C, Whitsett JA (1990) Structure and expression of the pulmonary surfactant protein SP-C gene in the mouse. J Biol Chem 265: 21986–21991.
Gossen M, Freundlieb S, Bender G, Muller G, Hillen W and Bujard H (1995) Transcriptional activation by tetracyclines in mammalian cells. Science 268: 1766–1769.
Honikel KO, Schmidt U, Woltersdorf W and Leistner L (1978) Effect of storage and processing on tetracycline residues in meat and bones. J Assoc Off Anal Chem 61: 1222–1227.
Jordan VC and Murphy CS (1990) Endocrine pharmacology of antiestrogens as antitumor agents. Endocr Rev 11: 578–610.
Kistner A, Gossen M, Zimmermann F, Jerecic J, Ullmer C, Lübbert H and Bujard H (1996) Doxycycline-mediated quantitative and tissue-specific control of gene expression in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93: 10933–10938.
Korsrud GO, Papich MG, Fesser AC, Salisbury CD and MacNeil JD (1996) Residue depletion in tissues and fluids from swine fed sulfamethazine, chlortetracycline and penicillin G in combination. Food Addit Contam 13: 287–292.
No D, Yao TP and Evans RM (1996) Ecdysone-inducible gene expression in mammalian cells and transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93: 3346–3351.
Picard D (1994) Regulation of protein function through expression of chimaeric proteins. Curr Opin Biotechnol 5: 511–515.
Porter A (1998) Controlling your losses: conditional gene silencing in mammals. Trends Genet 14: 73–79.
Ray P, Tang W, Wang P, Homer R, Kuhn C III, Flavell RA and Elias JA (1997) Regulated overexpression of interleukin 11 in the lung. Use to dissociate development-dependent and-independent phenotypes. J Clin Invest 100: 2501–2511.
Saez E, Nelson MC, Eshelman B, Banayo E, Koder A, Cho GJ and Evans RM (2000) Identification of ligands and coligands for the ecdysone-regulated gene switch. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97: 14512–14517.
Schultze N, Burki Y, Lang Y, Certa U and Bluethmann H (1996) Efficient control of gene expression by single step integration of the tetracycline system in transgenic mice. Nat Biotechnol 14: 499–503.
Spencer DM (1996) Creating conditional mutations in mammals. Trends Genet 12: 181–187.
Stripp BR, Sawaya PL, Luse DS, Wikenheiser KA, Wert SE, Huffman JA, Lattier DL, Singh G, Katayal SL and Whitsett JA (1992) Cis-acting elements that confer lung epithelial cell expression of the CC10 gene. J Biol Chem 267: 14703–14712.
Tichelaar JW, Lu W and Whitsett JA (2000) Conditional expression of fibroblast growth factor-7 in the developing and mature lung. J Biol Chem 275: 11858–11864.
Tsai SY, O'Malley BW, DeMayo FJ, Wang Y and Chua SS (1998) A novel RU486 inducible system for the activation and repression of genes. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 30: 23–31.
Wang Y, O'Malley BW Jr, Tsai SY and O'Malley BW (1994) A regulatory system for use in gene transfer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91: 8180–8184.
Wert SE, Glasser SW, Korfhagen TR and Whitsett JA (1993) Transcriptional elements from the human SP-C gene direct expression in the primordial respiratory epithelium of transgenic mice. Dev Biol 156: 426–443.
Whitsett JA and Glasser SW (1997) Targeting gene expression to the lung. In: Brigham LA (ed.) Gene Therapy for Diseases of the Lung (for the series: Lenfant C, editor. Lung Biology in Health and Disease). (pp. 193–208) Marcel Dekker, New York.
Zhou L, Dey CR, Wert SE, DuVall MD, Frizzell RA and Whitsett JA (1994) Correction of lethal intestinal defect in a mouse model of cystic fibrosis by human CFTR. Science 266: 1705–1708.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Perl, AK.T., Tichelaar, J.W. & Whitsett, J.A. Conditional gene expression in the respiratory epithelium of the mouse. Transgenic Res 11, 21–29 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1013986627504
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1013986627504