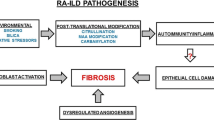
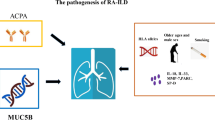
Abstract
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an inflammatory autoimmune disease characterized by the destruction of articular joint structures. RA is a systemic condition that often affects multiple organs, including the heart, lungs, and kidneys. Pulmonary complications of RA are relatively common and include pleural effusion, rheumatoid nodules, bronchiectasis, obliterative bronchiolitis, and opportunistic infections. Interstitial lung disease (ILD) is a common occurrence in patients with RA, and can range in severity from an asymptomatic incidental finding to a rapidly progressing life-threatening event. Usual interstitial pneumonia and non-specific interstitial pneumonia are the two most common patterns, though others have been reported. Various disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs—in particular, methotrexate and the tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibitors—have been associated with RA-ILD in numerous case reports and case series, though it is often difficult to distinguish association from causality. Treatment for RA-ILD typically involves the use of high-dose corticosteroids, often in conjunction with alternative immunosuppressant agents such as azathioprine or mycophenolate mofetil, and outcomes vary widely depending on the initial pattern of lung disease. Additional research into the mechanisms driving RA-ILD is needed to guide future therapy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Firestein GS. Evolving concepts of rheumatoid arthritis. Nature. 2003;423(6937):356–61.
Rothschild BM. Rheumatoid arthritis at a time of passage. J Rheumatol. 2001;28(2):245–50.
Prete M, Racanelli V, Digiglio L, Vacca A, Dammacco F, Perosa F. Extra-articular manifestations of rheumatoid arthritis: an update. Autoimmun Rev. 2011;11(2):123–31.
Myasoedova E, Crowson CS, Kremers HM, Therneau TM, Gabriel SE. Is the incidence of rheumatoid arthritis rising? Results from Olmsted County, Minnesota, 1955–2007. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62(6):1576–82.
Bharadwaj A, Haroon N. Interstitial lung disease and neuropathy as predominant extra-articular manifestations in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a prospective study. Med Sci Monit. 2005;11(10):CR498–502.
Norton S, Koduri G, Nikiphorou E, Dixey J, Williams P, Young A. A study of baseline prevalence and cumulative incidence of comorbidity and extra-articular manifestations in RA and their impact on outcome. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2013;52(1):99–110.
Young A, Koduri G. Extra-articular manifestations and complications of rheumatoid arthritis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2007;21(5):907–27.
Habib HM, Eisa AA, Arafat WR, Marie MA. Pulmonary involvement in early rheumatoid arthritis patients. Clin Rheumatol. 2011;30(2):217–21.
Rockall AG, Rickards D, Shaw PJ. Imaging of the pulmonary manifestations of systemic disease. Postgrad Med J. 2001;77(912):621–38.
Sidhu HS, Bhatnagar G, Bhogal P, Riordan R. Imaging features of the pleuropulmonary manifestations of rheumatoid arthritis: pearls and pitfalls. J Clin Imaging Sci. 2011;1:32.
Ishida T, Kotani T, Takeuchi T, Makino S. Pulmonary toxicity after initiation of azathioprine for treatment of interstitial pneumonia in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2012;39(5):1104–5.
Tsuchiya Y, Takayanagi N, Sugiura H, Miyahara Y, Tokunaga D, Kawabata Y, et al. Lung diseases directly associated with rheumatoid arthritis and their relationship to outcome. Eur Respir J. 2011;37(6):1411–7.
Balbir-Gurman A, Yigla M, Nahir AM, Braun-Moscovici Y. Rheumatoid pleural effusion. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2006;35(6):368–78.
Dascalu C, Mrejen-Shakin K, Bandagi S. Adalimumab-induced acute pneumonitis in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Rheumatol. 2010;16(4):172–4.
Nannini C, Medina-Velasquez YF, Achenbach SJ, Crowson CS, Ryu JH, Vassallo R, et al. Incidence and mortality of obstructive lung disease in rheumatoid arthritis: a population-based study. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2013;65(8):1243–50.
Devouassoux G, Cottin V, Liote H, Marchand E, Frachon I, Schuller A, et al. Characterisation of severe obliterative bronchiolitis in rheumatoid arthritis. Eur Respir J. 2009;33(5):1053–61.
White ES, Tazelaar HD, Lynch JP 3rd. Bronchiolar complications of connective tissue diseases. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2003;24(5):543–66.
Dixon WG, Hyrich KL, Watson KD, Lunt M, Symmons DP. Influence of anti-TNF therapy on mortality in patients with rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease: results from the British Society for Rheumatology Biologics Register. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;69(6):1086–91.
Leonel D, Lucia C, A M, Martha-Alicia H, Blanca M. Pulmonary function test: its correlation with pulmonary high-resolution computed tomography in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int. 2012;32(7):2111–6.
Mohd Noor N, Mohd Shahrir MS, Shahid MS, Abdul Manap R, Shahizon Azura AM, Azhar Shah S. Clinical and high resolution computed tomography characteristics of patients with rheumatoid arthritis lung disease. Int J Rheum Dis. 2009;12(2):136–44.
Olson AL, Swigris JJ, Sprunger DB, Fischer A, Fernandez-Perez ER, Solomon J, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis-interstitial lung disease-associated mortality. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2011;183(3):372–8.
Skare TL, Nakano I, Escuissiato DL, Batistetti R, Rodrigues Tde O, Silva MB. Pulmonary changes on high-resolution computed tomography of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and their association with clinical, demographic, serological and therapeutic variables. Rev Bras Reumatol. 2011;51(4):325–30, 36–7.
Zou YQ, Li YS, Ding XN, Ying ZH. The clinical significance of HRCT in evaluation of patients with rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease: a report from China. Rheumatol Int. 2012;32(3):669–73.
Bongartz T, Nannini C, Medina-Velasquez YF, Achenbach SJ, Crowson CS, Ryu JH, et al. Incidence and mortality of interstitial lung disease in rheumatoid arthritis: a population-based study. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62(6):1583–91.
Koduri G, Norton S, Young A, Cox N, Davies P, Devlin J, et al. Interstitial lung disease has a poor prognosis in rheumatoid arthritis: results from an inception cohort. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2010;49(8):1483–9.
Gochuico BR, Avila NA, Chow CK, Novero LJ, Wu HP, Ren P, et al. Progressive preclinical interstitial lung disease in rheumatoid arthritis. Arch Intern Med. 2008;168(2):159–66.
Furukawa H, Oka S, Shimada K, Sugii S, Ohashi J, Matsui T, et al. Association of human leukocyte antigen with interstitial lung disease in rheumatoid arthritis: a protective role for shared epitope. PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e33133.
Giles JT, Danoff SK, Sokolove J, Wagner CA, Winchester R, Pappas DA, et al. Association of fine specificity and repertoire expansion of anticitrullinated peptide antibodies with rheumatoid arthritis associated interstitial lung disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 2013.
Saag KG, Kolluri S, Koehnke RK, Georgou TA, Rachow JW, Hunninghake GW, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis lung disease: determinants of radiographic and physiologic abnormalities. Arthritis Rheum. 1996;39(10):1711–9.
Harlow L, Rosas IO, Gochuico BR, Mikuls TR, Dellaripa PF, Oddis CV, et al. Identification of citrullinated hsp90 isoforms as novel autoantigens in rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease. Arthritis Rheum. 2013;65(4):869–79.
Inui N, Enomoto N, Suda T, Kageyama Y, Watanabe H, Chida K. Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies in lung diseases associated with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Biochem. 2008;41(13):1074–7.
Mori S, Koga Y, Sugimoto M. Different risk factors between interstitial lung disease and airway disease in rheumatoid arthritis. Respir Med. 2012;106(11):1591–9.
Shidara K, Hoshi D, Inoue E, Yamada T, Nakajima A, Taniguchi A, et al. Incidence of and risk factors for interstitial pneumonia in patients with rheumatoid arthritis in a large Japanese observational cohort, IORRA. Mod Rheumatol. 2010;20(3):280–6.
Ito S, Sumida T. Interstitial lung disease associated with leflunomide. Intern Med. 2004;43(12):1103–4.
Xiangyang Z, Lutian Y, Lin Z, Liping X, Hui S, Jing L. Increased levels of interleukin-33 associated with bone erosion and interstitial lung diseases in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Cytokine. 2012;58(1):6–9.
Schwarz M, King TE, editors. Connective tissue diseases. 5th ed. Shelton: People’s Medical Publishing House; 2011.
Park IN, Kim DS, Shim TS, Lim CM, Lee SD, Koh Y, et al. Acute exacerbation of interstitial pneumonia other than idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Chest. 2007;132(1):214–20.
Morrison SC, Mody GM, Benatar SR, Meyers OL. The lungs in rheumatoid arthritis: a clinical, radiographic and pulmonary function study. S Afr Med J. 1996;86(7):829–33.
Walker WC, Wright V. Pulmonary lesions and rheumatoid arthritis. Medicine (Baltimore). 1968;47(6):501–20.
Cervantes-Perez P, Toro-Perez AH, Rodriguez-Jurado P. Pulmonary involvement in rheumatoid arthritis. JAMA. 1980;243(17):1715–9.
Dawson JK, Fewins HE, Desmond J, Lynch MP, Graham DR. Fibrosing alveolitis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis as assessed by high resolution computed tomography, chest radiography, and pulmonary function tests. Thorax. 2001;56(8):622–7.
Gabbay E, Tarala R, Will R, Carroll G, Adler B, Cameron D, et al. Interstitial lung disease in recent onset rheumatoid arthritis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1997;156(2 Pt 1):528–35.
Rojas-Serrano J, Gonzalez-Velasquez E, Mejia M, Sanchez-Rodriguez A, Carrillo G. Interstitial lung disease related to rheumatoid arthritis: evolution after treatment. Reumatol Clin. 2012;8(2):68–71.
Kim EJ, Collard HR, King TE Jr. Rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease: the relevance of histopathologic and radiographic pattern. Chest. 2009;136(5):1397–405.
Park JH, Kim DS, Park IN, Jang SJ, Kitaichi M, Nicholson AG, et al. Prognosis of fibrotic interstitial pneumonia: idiopathic versus collagen vascular disease-related subtypes. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007;175(7):705–11.
Lee HK, Kim DS, Yoo B, Seo JB, Rho JY, Colby TV, et al. Histopathologic pattern and clinical features of rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease. Chest. 2005;127(6):2019–27.
Kim EJ, Elicker BM, Maldonado F, Webb WR, Ryu JH, Van Uden JH, et al. Usual interstitial pneumonia in rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease. Eur Respir J. 2010;35(6):1322–8.
Nakamura Y, Suda T, Kaida Y, Kono M, Hozumi H, Hashimoto D, et al. Rheumatoid lung disease: prognostic analysis of 54 biopsy-proven cases. Respir Med. 2012;106(8):1164–9.
Solomon JJ, Ryu JH, Tazelaar HD, Myers JL, Tuder R, Cool CD, et al. Fibrosing interstitial pneumonia predicts survival in patients with rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease (RA-ILD). Respir Med. 2013;107(8):1247–52.
Flaherty KR, Colby TV, Travis WD, Toews GB, Mumford J, Murray S, et al. Fibroblastic foci in usual interstitial pneumonia: idiopathic versus collagen vascular disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2003;167(10):1410–5.
Turesson C, Matteson EL, Colby TV, Vuk-Pavlovic Z, Vassallo R, Weyand CM, et al. Increased CD4+ T cell infiltrates in rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial pneumonitis compared with idiopathic interstitial pneumonitis. Arthritis Rheum. 2005;52(1):73–9.
Choi HK, Hernan MA, Seeger JD, Robins JM, Wolfe F. Methotrexate and mortality in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a prospective study. Lancet. 2002;359(9313):1173–7.
Wasko MC, Dasgupta A, Hubert H, Fries JF, Ward MM. Propensity-adjusted association of methotrexate with overall survival in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2013;65(2):334–42.
Alarcon GS, Kremer JM, Macaluso M, Weinblatt ME, Cannon GW, Palmer WR, et al. Risk factors for methotrexate-induced lung injury in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a multicenter, case–control study. Methotrexate-Lung Study Group. Ann Intern Med. 1997;127(5):356–64.
Furukawa H, Oka S, Shimada K, Tsuchiya N, Tohma S. HLA-A*31:01 and methotrexate-induced interstitial lung disease in Japanese rheumatoid arthritis patients: a multidrug hypersensitivity marker? Ann Rheum Dis. 2013;72(1):153–5.
Saravanan V, Kelly C. Drug-related pulmonary problems in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2006;45(7):787–9.
Wolfe F, Caplan L, Michaud K. Rheumatoid arthritis treatment and the risk of severe interstitial lung disease. Scand J Rheumatol. 2007;36(3):172–8.
Chikura B, Lane S, Dawson JK. Clinical expression of leflunomide-induced pneumonitis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2009;48(9):1065–8.
Inokuma S. Leflunomide-induced interstitial pneumonitis might be a representative of disease-modifying antirheumatic drug-induced lung injury. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2011;10(4):603–11.
Sawada T, Inokuma S, Sato T, Otsuka T, Saeki Y, Takeuchi T, et al. Leflunomide-induced interstitial lung disease: prevalence and risk factors in Japanese patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2009;48(9):1069–72.
Suissa S, Hudson M, Ernst P. Leflunomide use and the risk of interstitial lung disease in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54(5):1435–9.
Horai Y, Miyamura T, Shimada K, Takahama S, Minami R, Yamamoto M, et al. Eternacept for the treatment of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and concurrent interstitial lung disease. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2012;37(1):117–21.
Perez-Alvarez R, Perez-de-Lis M, Diaz-Lagares C, Pego-Reigosa JM, Retamozo S, Bove A, et al. Interstitial lung disease induced or exacerbated by TNF-targeted therapies: analysis of 122 cases. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2011;41(2):256–64.
Pearce F, Johnson SR, Courtney P. Interstitial lung disease following certolizumab pegol. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2012;51(3):578–80.
Daien CI, Monnier A, Claudepierre P, Constantin A, Eschard JP, Houvenagel E, et al. Sarcoid-like granulomatosis in patients treated with tumor necrosis factor blockers: 10 cases. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2009;48(8):883–6.
Cho SK, Oh IH, Park CK, Bae SC, Sung YK. Etanercept induced organizing pneumonia in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int. 2012;32(4):1055–7.
Taki H, Kawagishi Y, Shinoda K, Hounoki H, Ogawa R, Sugiyama E, et al. Interstitial pneumonitis associated with infliximab therapy without methotrexate treatment. Rheumatol Int. 2009;30(2):275–6.
Yamazaki H, Isogai S, Sakurai T, Nagasaka K. A case of adalimumab-associated interstitial pneumonia with rheumatoid arthritis. Mod Rheumatol. 2010;20(5):518–21.
Herrinton LJ, Harrold LR, Liu L, Raebel MA, Taharka A, Winthrop KL, et al. Association between anti-TNF-alpha therapy and interstitial lung disease. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2013;22(4):394–402.
Ogiwara Y, Mochizuki H, Morioka T, Sugihara T, Makino F, Takahashi H. A case with life-threatening interstitial pneumonia associated with bucillamine treatment. Mod Rheumatol. 2008;18(5):522–5.
Koike R, Tanaka M, Komano Y, Sakai F, Sugiyama H, Nanki T, et al. Tacrolimus-induced pulmonary injury in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2011;24(4):401–6.
Vassallo R, Thomas CF. Advances in the treatment of rheumatic interstitial lung disease. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2004;16(3):186–91.
Antoniou KM, Mamoulaki M, Malagari K, Kritikos HD, Bouros D, Siafakas NM, et al. Infliximab therapy in pulmonary fibrosis associated with collagen vascular disease. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2007;25(1):23–8.
Furst DE, Keystone EC, So AK, Braun J, Breedveld FC, Burmester GR, et al. Updated consensus statement on biological agents for the treatment of rheumatic diseases, 2012. Ann Rheum Dis. 2013;72 Suppl 2:ii2–34.
Genovese MC, Breedveld FC, Emery P, Cohen S, Keystone E, Matteson EL, et al. Safety of biological therapies following rituximab treatment in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009;68(12):1894–7.
Kekow J, Moots RJ, Emery P, Durez P, Koenig A, Singh A, et al. Patient-reported outcomes improve with etanercept plus methotrexate in active early rheumatoid arthritis and the improvement is strongly associated with remission: the COMET trial. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;69(1):222–5.
Kelly C, Saravanan V. Treatment strategies for a rheumatoid arthritis patient with interstitial lung disease. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2008;9(18):3221–30.
Fischer A, Brown KK, Du Bois RM, Frankel SK, Cosgrove GP, Fernandez-Perez ER, et al. Mycophenolate mofetil improves lung function in connective tissue disease-associated interstitial lung disease. J Rheumatol. 2013;40(5):640–6.
Matteson EL, Choi HK, Poe DS, Wise C, Lowe VJ, McDonald TJ, et al. Etanercept therapy for immune-mediated cochleovestibular disorders: a multi-center, open-label, pilot study. Arthritis Rheum. 2005;53(3):337–42.
Gallelli L, Falcone D, Pelaia G, Renda T, Terracciano R, Malara N, et al. Interleukin-6 receptor superantagonist Sant7 inhibits TGF-beta-induced proliferation of human lung fibroblasts. Cell Prolif. 2008;41(3):393–407.
Mohr M, Jacobi AM. Interstitial lung disease in rheumatoid arthritis: response to IL-6R blockade. Scand J Rheumatol. 2011;40(5):400–1.
Acknowledgments
Dr Hallowell reports no conflict of interest. Dr Horton reports no conflict of interest. No sources of funding were used to support the writing of this review.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hallowell, R.W., Horton, M.R. Interstitial Lung Disease in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: Spontaneous and Drug Induced. Drugs 74, 443–450 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-014-0190-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-014-0190-z