Abstract
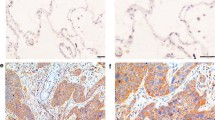
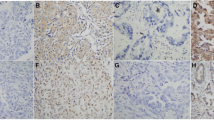
Ras/ERK and PI3K/Akt pathways are reported to play a prognostic role and contribute to drug resistance in many cancers. The objective of this study was to explore associations between the expression levels of several molecules in Ras/ERK and PI3K/Akt pathways and their clinical significance in predicting the effectiveness of postoperative adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). The expressions of K-ras, Raf-1, ERK1/2, phosphorylated ERK1/2 (pERK1/2), Akt-1, phosphorylated Akt-1 (pAkt-1), and Bcl-2 were detected by immunohistochemistry in tumor specimens from 144 NSCLC patients. The correlations between the expression levels of these molecules and the clinicopathological characteristics were analyzed. Patient survival was analyzed by Kaplan–Meier method, log-rank test, and Cox regression. The positive expression rates of K-ras, Raf-1, ERK1/2, pERK1/2, Akt-1, pAkt-1, and Bcl-2 were 21.5%, 41.7%, 59.7%, 27.1%, 50.7%, 36.1%, and 30.6%, respectively. Univariate analysis showed that patients with pERK1/2-positive (P = 0.01), Bcl-2-positive (P = 0.023), or pAkt-1 negative (P = 0.021) had significantly better recurrence-free survival (RFS) than those with pERK1/2-negative, Bcl-2-negative, or pAkt-1-positive. Multivariate analysis showed that earlier stage (P ≤ 0.001), non-adenocarcinoma (P ≤ 0.001), pERK1/2-positive (P ≤ 0.001), and pAkt-1-negative (P = 0.016) were independent prognostic factors for a better RFS in NSCLC. pERK1/2-positive and pAkt-1-negative proved to contribute to a better RFS in postoperative NSCLC patients who received adjuvant chemotherapy after taking the stage and histological subtype into account. pERK1/2 and pAkt-1 could be considered as new independent prognostic biomarkers for predicting RFS and selecting patients who are more likely to benefit from postoperative adjuvant chemotherapy.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, Murray T, et al. Cancer statistics, 2008. CA Cancer J Clin. 2008;58(2):71–96. doi:10.3322/CA.2007.0010.
Arriagada R, Bergman B, Dunant A, Le Chevalier T, Pignon JP, Vansteenkiste J, et al. Cisplatin-based adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with completely resected non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2004;350(4):351–60.
Winton T, Livingston R, Johnson D, Rigas J, Johnston M, Butts C, et al. Vinorelbine plus cisplatin vs. observation in resected non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2005;352(25):2589–97.
Douillard JY, Rosell R, De Lena M, Carpagnano F, Ramlau R, Gonzáles-Larriba JL, et al. Adjuvant vinorelbine plus cisplatin versus observation in patients with completely resected stage IB-IIIA non-small-cell lung cancer (Adjuvant Navelbine International Trialist Association [ANITA]): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2006;7(9):719–27.
Hotta K, Matsuo K, Ueoka H, Kiura K, Tabata M, Tanimoto M. Role of adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with resected non-small-cell lung cancer: reappraisal with a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22(19):3860–7. doi:10.1200/JCO.2004.01.153.
Simon GR, Sharma S, Cantor A, Smith P, Bepler G. ERCC1 expression is a predictor of survival in resected patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Chest. 2005;127(3):978–83. doi:10.1378/chest.127.3.978.
Lee KH, Min HS, Han SW, Oh DY, Lee SH, Kim DW, et al. ERCC1 expression by immunohistochemistry and EGFR mutations in resected non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2008;60(3):401–7. doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2007.10.014.
Olaussen KA, Dunant A, Fouret P, Brambilla E, André F, Haddad V, et al. DNA repair by ERCC1 in non-small-cell lung cancer and cisplatin-based adjuvant chemotherapy. N Engl J Med. 2006;355(10):983–91.
Breen D, Barlési F. The place of excision repair cross complementation 1 (ERCC1) in surgically treated non-small cell lung cancer. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2008;33(5):805–11. doi:10.1016/j.ejcts.2008.01.067.
Sève P, Lai R, Ding K, Winton T, Butts C, Mackey J, et al. Class III beta-tubulin expression and benefit from adjuvant cisplatin/vinorelbine chemotherapy in operable non-small cell lung cancer: analysis of NCIC JBR.10. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13(3):994–9.
McCubrey JA, Steelman LS, Abrams SL, Lee JT, Chang F, Bertrand FE, et al. Roles of the RAF/MEK/ERK and PI3K/PTEN/AKT pathways in malignant transformation and drug resistance. Adv Enzyme Regul. 2006;46:249–79. doi:10.1016/j.advenzreg.2006.01.004.
Cappuzzo F, Hirsch FR, Rossi E, Bartolini S, Ceresoli GL, Bemis L, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor gene and protein and gefitinib sensitivity in non-small-cell lung cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2005;97(9):643–55. doi:10.1093/jnci/dji112.
Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, Gurubhagavatula S, Okimoto RA, Brannigan BW, et al. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 2004;350(21):2129–39.
Pao W, Wang TY, Riely GJ, Miller VA, Pan Q, Ladanyi M, et al. KRAS mutations and primary resistance of lung adenocarcinomas to gefitinib or erlotinib. PLoS Med. 2005;2(1):57–61. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.0020017.
Sordella R, Bell DW, Haber DA, Settleman J. Gefitinib-sensitizing EGFR mutations in lung cancer activate anti-apoptotic pathways. Science. 2004;305(5687):1163–7. doi:10.1126/science.1101637.
Eberhard DA, Johnson BE, Amler LC, Goddard AD, Heldens SL, Herbst RS, et al. Mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor and in KRAS are predictive and prognostic indicators in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer treated with chemotherapy alone and in combination with erlotinib. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23(25):5900–9. doi:10.1200/JCO.2005.02.857.
Massarelli E, Varella-Garcia M, Tang XM, Xavier AC, Ozburn NC, Liu DD, et al. KRAS mutation is an important predictor of resistance to therapy with epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13(10):2890–6. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-3043.
David O, Jett J, LeBeau H, Dy G, Hughes J, Friedman M, et al. Phospho-Akt overexpression in non-small cell lung cancer confers significant stage-independent survival disadvantage. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10(20):6865–71. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-0174.
Galleges Ruiz MI, Floor K, Steinberg SM, Grünberg K, Thunnissen FB, Belien JA, et al. Combined assessment of EGFR pathway-related molecular markers and prognosis of NSCLC patients. Br J Cancer. 2009;100(1):145–52. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6604781.
Davis JM, Weinstein-Oppenheimer CR, Steelman LS, Navolanic PN, Hu W, Konopleva M, et al. Raf-1 and Bcl-2 induce distinct and common pathways which contribute to breast cancer drug resistance. Clin Cancer Res. 2003;9(3):1161–70.
Lee JT, Steelman LS, McCubrey JA. Modulation of Raf/MEK/ERK pathway in prostate cancer drug resistance. Int J Oncol. 2005;26(6):1637–44.
Lee JT, Steelman LS, McCubrey JA. Phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase activation leads to multidrug resistance protein-1 expression and subsequent chemoresistance in advanced prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2004;64(22):8397–404. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-1612.
Turner BC, Krajewski S, Krajewska M, Takayama S, Gumbs AA, Carter D, et al. BAG-1: a novel biomarker predicting long-term survival in early-stage breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2001;19(4):992–1000.
Rakha EA, Abd El Rehim D, Pinder SE, Lewis SA, Ellis IO. E-Cadherin expression in invasive non-lobular carcinoma of the breast and its prognostic significance. Histopathology. 2005;46(6):685–93. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2559.2005.02156.x.
Goss GD, Lorimer I, Tsao MS, O’Callaghan CJ, Ding K, Masters GA, et al. A phase III randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of the epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor gefitinib in completely resected stage IB-IIIA non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): NCIC CTG BR.19. J Clin Oncol ASCO Annual Meeting Proceedings. 2010;28(18suppl):LBA7005.
Dhillon AS, Hagan S, Rath O, Kolch W. MAP kinase signalling pathways in cancer. Oncogene. 2007;26(22):3279–90. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1210421.
Roberts PJ, Der CJ. Targeting the Raf-MEK-ERK mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade for the treatment of cancer. Oncogene. 2007;26(22):3291–310. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1210422.
Han SW, Kim TY, Hwang PG, Jeong S, Kim J, Choi IS, et al. Predictive and prognostic impact of epidermal growth factor receptor mutation in non-small-cell lung cancer patients treated with gefitinib. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23(11):2493–501. doi:10.1200/JCO.2005.01.388.
Han SW, Kim TY, Jeon YK, Hwang PG, Im SA, Lee KH, et al. Optimization of patient selection for gefitinib in non-small cell lung cancer by combined analysis of epidermal growth factor receptor mutation, K-ras mutation, and Akt phosphorylation. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12(8):2538–44. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-2845.
Vicent S, Lopez-Picazo JM, Toledo G, Lozano MD, Torre W, Garcia-Corchón C, et al. ERK1/2 is activated in non-small-cell lung cancer and associated with advanced tumours. Br J Cancer. 2004;90(5):1047–52. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6601644.
Mukohara T, Kudoh S, Yamauchi S, Kimura T, Yoshimura N, Kanazawa H, et al. Expression of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and downstream-activated peptides in surgically excised non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Lung Cancer. 2003;41(2):123–30. doi:10.1016/S0169-5002(03)00225-3.
Altomare DA, Testa JR. Perturbations of the AKT signaling pathway in human cancer. Oncogene. 2005;24(50):7455–64. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1209085.
Tsurutani J, Fukuoka J, Tsurutani H, Shih JH, Hewitt SM, Travis WD, et al. Evaluation of two phosphorylation sites improves the prognostic significance of Akt activation in non-small-cell lung cancer tumors. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24(2):306–14. doi:10.1200/JCO.2005.02.4133.
Brognard J, Clark AS, Ni Y, Dennis PA. Akt/protein kinase B is constitutively active in non-small cell lung cancer cells and promotes cellular survival and resistance to chemotherapy and radiation. Cancer Res. 2001;61(10):3986–97.
Tu ML, Wang HQ, Chen LJ, Lu JC, Jiang F, Liang JH, et al. Involvement of Akt1/protein kinase Balpha in tumor conditioned medium-induced endothelial cell migration and survival in vitro. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2009;135(11):1543–50. doi:10.1007/s00432-009-0601-9.
Yoshizawa A, Fukuoka J, Shimizu S, Shilo K, Franks TJ, Hewitt SM, et al. Overexpression of phospho-eIF4E is associated with survival through AKT pathway in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2010;16(1):240–8. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-0986.
Tang JM, He QY, Guo RX, Chang XJ. Phosphorylated Akt overexpression and loss of PTEN expression in non-small cell lung cancer confers poor prognosis. Lung Cancer. 2006;51(2):181–91. doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2005.10.003.
Haas-Kogan DA, Prados MD, Lamborn KR, Tihan T, Berger MS, Stokoe D. Biomarkers to predict response to epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors. Cell Cycle. 2005;4(10):1369–72.
Anderson NG, Ahmad T, Chan K, Dobson R, Bundred NJ. ZD1839 (Iressa), a novel epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor, potently inhibits the growth of EGFR-positive cancer cell lines with or without erbB2 overexpression. Int J Cancer. 2001;94:774–82.
Albanell J, Rojo F, Baselga J. Pharmacodynamic studies with the epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor ZD1839. Semin Oncol. 2001;28:56–66.
Janmaat ML, Kruyt FA, Rodriguez JA, Giaccone G. Response to epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer cells: limited antiproliferative effects and absence of apoptosis associated with persistent activity of extracellular signal-regulated kinase or Akt kinase pathways. Clin Cancer Res. 2003;9(6):2316–26.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Key Project of the “Eleventh Five-year Plan” for Medical Science Development of CPLA of China (Shun-Chang Jiao, NO. 06G106) and Cancer Target Therapy Project of Jie-Ping Wu Fund of China (Yan Shi, NO. 320.6700.09006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, Y., Chen, L., Li, J. et al. Prognostic and predictive values of pERK1/2 and pAkt-1 expression in non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with adjuvant chemotherapy. Tumor Biol. 32, 381–390 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-010-0131-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-010-0131-8