Abstract
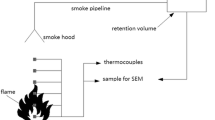
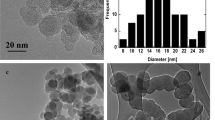
The elemental carbon core of combustion particles is covered with more or less volatile material, depending on the emission source, and these coatings could have a significant influence on the optical and hygroscopic nature of the soot particles. Detailed soot characteristics are therefore highly dependent on the formation conditions and on the combustion process and some intrinsic characteristics are different for soot of different sources. Although morphological studies on soot aggregates have a long and elaborate history, based mainly on simulations, the application of image analysis on individual soot particles has been limited. The purpose of this work is to detect whether there are significant differences in morphology between soot aggregates from different origins. By performing individual particle analysis, the morphology is measured on single particles and these particles are characterized as a function of their aerodynamic diameter. In this paper, a description of an irregular shape of aggregate is performed by applying the developed image analysis methodology to electron microscopical images. Some new parameters are defined and a method is established to calculate the number of primary particles in a soot aggregate produced by different sources. These provided a means to distinguish between different soot types and their corresponding production conditions.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bérubé, K.A., Jones, T.P., Williamson, B.J., Morgan, A.J., Richards, R.J.: Physicochemical characterisation of diesel exhaust particles; factor for assessing biological activity. Atmos. Environ. 33, 1599–1614 (1999)
Brasil, A.M., Farais, T.L., Carvalho, M.G., Koylu, U.O.: Numerical characterization of the morphology of aggregated particles. J. Aerosol Sci. 32, 489–508 (2001)
Chylek, P., Ramaswany, V., Cheng, R.J.: Effect of graphitic carbon on the albedo of clouds. J. Atmos. Sci. 41, 3076–3084 (1984)
Cleary, T., Pao, J.-R., Mulholland, G., Gentry, J.W.: Measurement and simulation of soot agglomerates and clusters. J. Aerosol Sci. 20, 871–874 (1989)
Dobbins, R.A., Mulholland, G.W., Bryner, N.P.: Comparison of a fractal smoke optics model with light extinction measurements. Atmos. Environ. 28, 889–897 (1994)
Gruber, T.C., Herd, C.R.: Anisometry measurements in carbon black aggregate populations. Rubber Chem. Technol. 70, 727–746 (1997)
Gruber, T.C., Zerda, T.W., Gerspacher, M.: 3D morphological characterisation of carbon-black aggregates using transmission electron microscopy. Rubber Chem. Technol. 67, 280–287 (1994)
Hueglin, C., Scherrer, L., Burtscher, H.: An accurate continuously adjustable dilution system (1:10 to 1:10E4) for submicron aerosols. J. Aerosol Sci. 28, 1049–1055 (1997)
Keskinen, J., Virtanen, A., Ahlvik, P., Ntziachrstos, L.L.: Estimation of effective density of diesel particles. J. Aerosol Sci. 29, S1007–S1008 (1998)
Kops, J.A.M.M.: The aerodynamic diameter and specific surface area of branched chain-like aggregates. PhD thesis, University of Eindhoven, vol. 89, pp. 140–156 (1976)
Lammel, G., Novakov, T.: Water nucleation properties of carbon black and diesel soot particles. Atmos. Environ. 29, 813–823 (1995)
Marple, V.A., Rubow, K.L., Olson, B.A.: In: Klaus, W., Baron, P.A. (eds.) Aerosol Measurements: Principles, Techniques and Applications, pp. 206–232. Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York (1993)
McMurry, P.H., Wang, X., Park, K., Ehara, K.: The relationship between mass and mobility for atmospheric particles: a new technique for measuring particle density. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 36, 227–238 (2002)
Medalia, A.I., Heckman, F.A.: Morphology of aggregates. II. Size and shape factors of carbon black aggregates from electron microscopy. Carbon 7, 567–582 (1969)
Pandis, S.N., Wexler, A.S., Seinfeld, J.H.: Dynamics of tropospheric aerosols. J. Phys. Chem. 99, 9646–9659 (1995)
Petzgold, A., Schröder, F.P.: Jet engine exhaust aerosol characterisation. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 28, 62–76 (1998)
Reid, J.S., Cahill, T.A., Wakabayashi, P.H., Dunlap, M.R.: Geometric/aerodynamic equivalent diameter ratios of ash aggregate aerosols collected in burning Kuwaiti well fields. Atmos. Environ. 28, 2227–2234 (1994)
Ulfvarson, U., Figler, B., Krantz, S.: Diesel Engine Development is Guided by Inadequate Particle Sampling, SAE paper no. 970759, pp. 79–92. Society of Automative Engineers, Warrendale, PA (1997)
US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA): Health assessment document for diesel engine exhaust. Prepared by the National Center for Environmental Assessment, Washington, DC, for the Office of Transportation and Air Quality; EPA/600/8-90/057F. Available from: National Technical Information Service, Springfield, VA; PB2002-107661, and <http://www.epa.gov/ncea> (2002)
Zier, M., Götz, D.: Ein Verfahren zur Bestimmung der Asbest-und Russkonzentration in der Atmosphäre mit Hilfe der Transmissionelektronenmikroskopie. Zeitschrift für Gezundheitstechnik und Hygiene 28, 585–862 (1982)
Acknowledgements
The authors are very grateful to the Flemish Institute for Technological Research (VITO) for the grant to Anne Smekens. The authors express their appreciation to Dr J. Marijnissen of the Delft Technical University for the use of the spiral aerosol centrifuge and to Dr P. Ngendakumana of Université de Liège for his cooperation. The authors also wish to thank the Royal Belgian Air Force for the sampling of the soot of a jet aircraft engine.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smekens, A., Godoi, R.H.M., Vervoort, M. et al. Characterization of Individual Soot Aggregates from Different Sources using Image Analysis. J Atmos Chem 56, 211–223 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10874-006-9050-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10874-006-9050-x