Abstract
Lung cancers that harbor somatic activating mutations in the gene for the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) depend on mutant EGFR for their proliferation and survival; therefore, lung cancer patients with EGFR mutations often dramatically respond to orally available EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs). However, emergence of acquired resistance is virtually inevitable, thus limiting improvement in patient outcomes. To elucidate and overcome this acquired resistance, multidisciplinary basic and clinical investigational approaches have been applied, using in vitro cell line models or samples obtained from lung cancer patients treated with EGFR-TKIs. These efforts have revealed several acquired resistance mechanisms and candidates, including EGFR secondary mutations (T790M and other rare mutations), MET amplification, PTEN downregulation, CRKL amplification, high-level HGF expression, FAS–NFκB pathway activation, epithelial–mesenchymal transition, and conversion to small cell lung cancer. Interestingly, cancer cells harbor potential destiny and ductility together in acquiring resistance to EGFR-TKIs, as shown in in vitro acquired resistance models. Molecular mechanisms of “reversible EGFR-TKI tolerance” that occur in early phase EGFR-TKI exposure have been identified in cell line models. Furthermore, others have reported molecular markers that can predict response to EGFR-TKIs in clinical settings. Deeper understanding of acquired resistance mechanisms to EGFR-TKIs, followed by the development of molecular target drugs that can overcome the resistance, might turn this fatal disease into a chronic disorder.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pao, W., & Girard, N. (2011). New driver mutations in non-small-cell lung cancer. The Lancet Oncology, 12, 175–180.
Weinstein, I. B. (2002). Cancer. Addiction to oncogenes—the Achilles heal of cancer. Science, 297, 63–64.
Suda, K., Tomizawa, K., & Mitsudomi, T. (2010). Biological and clinical significance of KRAS mutations in lung cancer: an oncogenic driver that contrasts with EGFR mutation. Cancer and Metastasis Reviews, 29, 49–60.
Mitsudomi, T., Morita, S., Yatabe, Y., Negoro, S., Okamoto, I., Tsurutani, J., et al. (2010). Gefitinib versus cisplatin plus docetaxel in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring mutations of the epidermal growth factor receptor (WJTOG3405): an open label, randomised phase 3 trial. The Lancet Oncology, 11, 121–128.
Maemondo, M., Inoue, A., Kobayashi, K., Sugawara, S., Oizumi, S., Isobe, H., et al. (2010). Gefitinib or chemotherapy for non-small-cell lung cancer with mutated EGFR. The New England Journal of Medicine, 362, 2380–2388.
Zhou, C., Wu, Y. L., Chen, G., Feng, J., Liu, X. Q., Wang, C., et al. (2011). Erlotinib versus chemotherapy as first-line treatment for patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (OPTIMAL, CTONG-0802): a multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3 study. The Lancet Oncology, 12, 735–742.
Rosell, R., Carcereny, E., Gervais, R., Vergnenegre, A., Massuti, B., Felip, E., et al. (2012). Erlotinib versus standard chemotherapy as first-line treatment for European patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (EURTAC): a multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. The Lancet Oncology, 13, 239–246.
Jackman, D., Pao, W., Riely, G. J., Engelman, J. A., Kris, M. G., Janne, P. A., et al. (2010). Clinical definition of acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in non-small-cell lung cancer. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 28, 357–360.
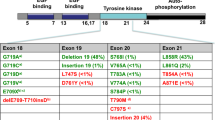
Kobayashi, S., Boggon, T. J., Dayaram, T., Janne, P. A., Kocher, O., Meyerson, M., et al. (2005). EGFR mutation and resistance of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. The New England Journal of Medicine, 352, 786–792.
Blencke, S., Ullrich, A., & Daub, H. (2003). Mutation of threonine 766 in the epidermal growth factor receptor reveals a hotspot for resistance formation against selective tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 278, 15435–15440.
Arcila, M. E., Oxnard, G. R., Nafa, K., Riely, G. J., Solomon, S. B., Zakowski, M. F., et al. (2011). Rebiopsy of lung cancer patients with acquired resistance to EGFR inhibitors and enhanced detection of the T790M mutation using a locked nucleic acid-based assay. Clinical Cancer Research, 17, 1169–1180.
Yun, C. H., Mengwasser, K. E., Toms, A. V., Woo, M. S., Greulich, H., Wong, K. K., et al. (2008). The T790M mutation in EGFR kinase causes drug resistance by increasing the affinity for ATP. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 105, 2070–2075.
Chmielecki, J., Foo, J., Oxnard, G. R., Hutchinson, K., Ohashi, K., Somwar, R., et al. (2011). Optimization of dosing for EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer with evolutionary cancer modeling. Science Translational Medicine, 3, 90ra59.
Suda, K., Onozato, R., Yatabe, Y., & Mitsudomi, T. (2009). EGFR T790M mutation: a double role in lung cancer cell survival? Journal of Thoracic Oncology, 4, 1–4.
Oxnard, G. R., Arcila, M. E., Sima, C. S., Riely, G. J., Chmielecki, J., Kris, M. G., et al. (2011). Acquired resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in EGFR-mutant lung cancer: distinct natural history of patients with tumors harboring the T790M mutation. Clinical Cancer Research, 17, 1616–1622.
Uramoto, H., Yano, S., & Tanaka, F. (2012). T790M is associated with a favorable prognosis in Japanese patients treated with an EGFR-TKI. Lung Cancer, 76, 129–130.
Balak, M. N., Gong, Y., Riely, G. J., Somwar, R., Li, A. R., Zakowski, M. F., et al. (2006). Novel D761Y and common secondary T790M mutations in epidermal growth factor receptor-mutant lung adenocarcinomas with acquired resistance to kinase inhibitors. Clinical Cancer Research, 12, 6494–6501.
Costa, D. B., Halmos, B., Kumar, A., Schumer, S. T., Huberman, M. S., Boggon, T. J., et al. (2007). BIM mediates EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor-induced apoptosis in lung cancers with oncogenic EGFR mutations. PLoS Medicine, 4, 1669–1679. discussion 80.
Bean, J., Riely, G. J., Balak, M., Marks, J. L., Ladanyi, M., Miller, V. A., et al. (2008). Acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor kinase inhibitors associated with a novel T854A mutation in a patient with EGFR-mutant lung adenocarcinoma. Clinical Cancer Research, 14, 7519–7525.
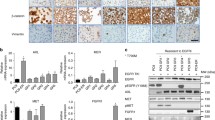
Engelman, J. A., Zejnullahu, K., Mitsudomi, T., Song, Y., Hyland, C., Park, J. O., et al. (2007). MET amplification leads to gefitinib resistance in lung cancer by activating ERBB3 signaling. Science, 316, 1039–1043.
Sequist, L. V., Waltman, B. A., Dias-Santagata, D., Digumarthy, S., Turke, A. B., Fidias, P., et al. (2011). Genotypic and histological evolution of lung cancers acquiring resistance to EGFR inhibitors. Science Translational Medicine, 3, 75ra26.
Onozato, R., Kosaka, T., Kuwano, H., Sekido, Y., Yatabe, Y., & Mitsudomi, T. (2009). Activation of MET by gene amplification or by splice mutations deleting the juxtamembrane domain in primary resected lung cancers. Journal of Thoracic Oncology, 4, 5–11.
Tanizaki, J., Okamoto, I., Okamoto, K., Takezawa, K., Kuwata, K., Yamaguchi, H., et al. (2011). MET tyrosine kinase inhibitor crizotinib (PF-02341066) shows differential antitumor effects in non-small cell lung cancer according to MET alterations. Journal of Thoracic Oncology, 6, 1624–1631.
Yamamoto, C., Basaki, Y., Kawahara, A., Nakashima, K., Kage, M., Izumi, H., et al. (2010). Loss of PTEN expression by blocking nuclear translocation of EGR1 in gefitinib-resistant lung cancer cells harboring epidermal growth factor receptor-activating mutations. Cancer Research, 70, 8715–8725.
Suda, K., Tomizawa, K., Osada, H., Maehara, Y., Yatabe, Y., Sekido, Y., et al. (2012). Conversion from the “oncogene addiction” to “drug addiction” by intensive inhibition of the EGFR and MET in lung cancer with activating EGFR mutation. Lung Cancer, 76, 292–299.
Uramoto, H., Shimokawa, H., Hanagiri, T., Kuwano, M., & Ono, M. (2011). Expression of selected gene for acquired drug resistance to EGFR-TKI in lung adenocarcinoma. Lung Cancer, 73, 361–365.
Cheung, H. W., Du, J., Boehm, J. S., He, F., Weir, B. A., Wang, X., et al. (2011). Amplification of CRKL induces transformation and epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor resistance in human non-small cell lung cancers. Cancer Discovery, 1, 608–625.
Yano, S., Wang, W., Li, Q., Matsumoto, K., Sakurama, H., Nakamura, T., et al. (2008). Hepatocyte growth factor induces gefitinib resistance of lung adenocarcinoma with epidermal growth factor receptor-activating mutations. Cancer Research, 68, 9479–9487.
Yano, S., Yamada, T., Takeuchi, S., Tachibana, K., Minami, Y., Yatabe, Y., et al. (2011). Hepatocyte growth factor expression in EGFR mutant lung cancer with intrinsic and acquired resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors in a Japanese cohort. Journal of Thoracic Oncology, 6(12), 2011–2017.
Bivona, T. G., Hieronymus, H., Parker, J., Chang, K., Taron, M., Rosell, R., et al. (2011). FAS and NF-kappaB signalling modulate dependence of lung cancers on mutant EGFR. Nature, 471, 523–526.
Liu, D., Huang, C., Kameyama, K., Hayashi, E., Yamauchi, A., Kobayashi, S., et al. (2001). E-cadherin expression associated with differentiation and prognosis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. The Annals of Thoracic Surgery, 71, 949–954. discussion 54–5.
Bremnes, R. M., Veve, R., Gabrielson, E., Hirsch, F. R., Baron, A., Bemis, L., et al. (2002). High-throughput tissue microarray analysis used to evaluate biology and prognostic significance of the E-cadherin pathway in non-small-cell lung cancer. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 20, 2417–2428.
Yang, J., Mani, S. A., Donaher, J. L., Ramaswamy, S., Itzykson, R. A., Come, C., et al. (2004). Twist, a master regulator of morphogenesis, plays an essential role in tumor metastasis. Cell, 117, 927–939.
Kang, Y., & Massague, J. (2004). Epithelial–mesenchymal transitions: twist in development and metastasis. Cell, 118, 277–279.
Chung, J. H., Rho, J. K., Xu, X., Lee, J. S., Yoon, H. I., Lee, C. T., et al. (2011). Clinical and molecular evidences of epithelial to mesenchymal transition in acquired resistance to EGFR-TKIs. Lung Cancer, 73, 176–182.
Suda, K., Tomizawa, K., Fujii, M., Murakami, H., Osada, H., Maehara, Y., et al. (2011). Epithelial to mesenchymal transition in an epidermal growth factor receptor-mutant lung cancer cell line with acquired resistance to erlotinib. Journal of Thoracic Oncology, 6, 1152–1161.
Yao, Z., Fenoglio, S., Gao, D. C., Camiolo, M., Stiles, B., Lindsted, T., et al. (2010). TGF-beta IL-6 axis mediates selective and adaptive mechanisms of resistance to molecular targeted therapy in lung cancer. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 107, 15535–15540.
Chang, T. H., Tsai, M. F., Su, K. Y., Wu, S. G., Huang, C. P., Yu, S. L., et al. (2011). Slug confers resistance to the epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, 183, 1071–1079.
Xie, M., Zhang, L., He, C. S., Xu, F., Liu, J. L., Hu, Z. H., et al. (2012). Activation of Notch-1 enhances epithelial–mesenchymal transition in gefitinib-acquired resistant lung cancer cells. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry, 113(5), 1501–1513.
Inukai, M., Toyooka, S., Ito, S., Asano, H., Ichihara, S., Soh, J., et al. (2006). Presence of epidermal growth factor receptor gene T790M mutation as a minor clone in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Research, 66, 7854–7858.
Maheswaran, S., Sequist, L. V., Nagrath, S., Ulkus, L., Brannigan, B., Collura, C. V., et al. (2008). Detection of mutations in EGFR in circulating lung-cancer cells. The New England Journal of Medicine, 359, 366–377.
Turke, A. B., Zejnullahu, K., Wu, Y. L., Song, Y., Dias-Santagata, D., Lifshits, E., et al. (2010). Preexistence and clonal selection of MET amplification in EGFR mutant NSCLC. Cancer Cell, 17, 77–88.
Suda, K., Murakami, I., Katayama, T., Tomizawa, K., Osada, H., Sekido, Y., et al. (2010). Reciprocal and complementary role of MET amplification and EGFR T790M mutation in acquired resistance to kinase inhibitors in lung cancer. Clinical Cancer Research, 16, 5489–5498.
Ogino, A., Kitao, H., Hirano, S., Uchida, A., Ishiai, M., Kozuki, T., et al. (2007). Emergence of epidermal growth factor receptor T790M mutation during chronic exposure to gefitinib in a non small cell lung cancer cell line. Cancer Research, 67, 7807–7814.
Ercan, D., Zejnullahu, K., Yonesaka, K., Xiao, Y., Capelletti, M., Rogers, A., et al. (2010). Amplification of EGFR T790M causes resistance to an irreversible EGFR inhibitor. Oncogene, 29, 2346–2356.
Sharma, S. V., Lee, D. Y., Li, B., Quinlan, M. P., Takahashi, F., Maheswaran, S., et al. (2010). A chromatin-mediated reversible drug-tolerant state in cancer cell subpopulations. Cell, 141, 69–80.
Fan, W., Tang, Z., Yin, L., Morrison, B., Hafez-Khayyata, S., Fu, P., et al. (2011). MET-independent lung cancer cells evading EGFR kinase inhibitors are therapeutically susceptible to BH3 mimetic agents. Cancer Research, 71, 4494–4505.
Ng, K. P., Hillmer, A. M., Chuah, C. T., Juan, W. C., Ko, T. K., Teo, A. S., et al. (2012). A common BIM deletion polymorphism mediates intrinsic resistance and inferior responses to tyrosine kinase inhibitors in cancer. Nature Medicine, 18, 521–528.
Kurata, T., Tamura, K., Kaneda, H., Nogami, T., Uejima, H., Asai Go, G., et al. (2004). Effect of re-treatment with gefitinib (‘Iressa’, ZD1839) after acquisition of resistance. Annals of Oncology, 15, 173–174.
Yano, S., Nakataki, E., Ohtsuka, S., Inayama, M., Tomimoto, H., Edakuni, N., et al. (2005). Retreatment of lung adenocarcinoma patients with gefitinib who had experienced favorable results from their initial treatment with this selective epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor: a report of three cases. Oncology Research, 15, 107–111.
Choi, Y. L., Soda, M., Yamashita, Y., Ueno, T., Takashima, J., Nakajima, T., et al. (2011). EML4-ALK mutations in lung cancer that confer resistance to ALK inhibitors. The New England Journal of Medicine, 363, 1734–1739.
Katayama, R., Shaw, A. T., Khan, T. M., Mino-Kenudson, M., Solomon, B. J., Halmos, B., et al. (2012). Mechanisms of acquired crizotinib resistance in ALK-rearranged lung Cancers. Science Translational Medicine, 4, 120ra17.
Yoshida, T., Okamoto, I., Okamoto, W., Hatashita, E., Yamada, Y., Kuwata, K., et al. (2010). Effects of Src inhibitors on cell growth and epidermal growth factor receptor and MET signaling in gefitinib-resistant non-small cell lung cancer cells with acquired MET amplification. Cancer Science, 101, 167–172.
Kobayashi, N., Toyooka, S., Soh, J., Yamamoto, H., Dote, H., Kawasaki, K., et al. (2011). The anti-proliferative effect of heat shock protein 90 inhibitor, 17-DMAG, on non-small-cell lung cancers being resistant to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Lung Cancer, 75, 161–166.
Ju, L., Zhou, C., Li, W., Yan, L. (2010). Integrin beta1 over-expression associates with resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitor gefitinib in non-small cell lung cancer. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry, 111, 1565–1574.
Acknowledgment
This study is supported in part by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (B) from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (23390340).
Disclosure of potential conflict of interest
Dr. Mitsudomi has received lecture fees from AstraZeneca and Chugai. The other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This study is supported in part by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (B) from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (23390340).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suda, K., Mizuuchi, H., Maehara, Y. et al. Acquired resistance mechanisms to tyrosine kinase inhibitors in lung cancer with activating epidermal growth factor receptor mutation—diversity, ductility, and destiny. Cancer Metastasis Rev 31, 807–814 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-012-9391-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-012-9391-7