Abstract
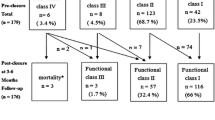
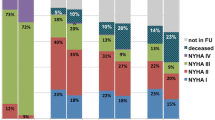
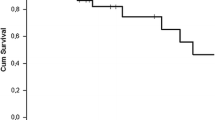
We investigated the short-term and medium-term results in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) associated with atrial septal defect (ASD) undergoing transcatheter closure. Fifteen patients with severe PAH associated with ASD who underwent successful occluder implantation from 2007 to 2010 were included. Clinical, echocardiographic, and hemodynamic data were reviewed. Severe PAH was defined as pulmonary arterial systolic pressure measured by catheterization was ≥60 mmHg and pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR) ≥6 Wood Units (WU). Compared with baseline, the 6-minwalking distance significantly increased by 29.7 ± 26.3 m (P < 0.001) at 3 months (short-term) and 65.4 ± 63.6 m (P < 0.001) at 23.4 ± 9.7 months (medium-term), World Health Organization function class considerably improved after postclosure short-term and medium-term. Repeat cardiac catheterization (n = 7) showed that mean pulmonary arterial pressure decreased from 51.6 ± 9.4 mmHg at baseline to 21.0 ± 3.8 mmHg (P < 0.001) at follow-up of 12 months. The PVR decreased by 5.6 ± 1.1 WU (P < 0.001). Through carefully selected patients with severe PAH associated with ASD, transcatheter closure can be safely performed with a promising short-term and medium-term outcome. Trial occlusion is an effective way for deciding the reversibility of severe PAH in ASD patients. The role of aerosolized iloprost for pulmonary vasoreactivity testing in patients with severe PAH secondary to ASD requires further investigation.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barst RJ, McGoon M, Torbicki A, Sitbon O, Krowka MJ, Olschewski H, Gaine S (2004) Diagnosis and differential assessment of pulmonary arterial hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol 43:40S–47S
Humbert M, Sitbon O, Chaouat A, Bertocchi M, Habib G, Gressin V, Yaici A, Weitzenblum E, Cordier JF, Chabot F, Dromer C, Pison C, Reynaud-Gaubert M, Haloun A, Laurent M, Hachulla E, Simonneau G (2006) Pulmonary arterial hypertension in France: results from a national registry. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 173:1023–1030
Bush A, Busst CM, Haworth SG, Hislop AA, Knight WB, Corrin B, Shinebourne EA (1988) Correlations of lung morphology, pulmonary vascular resistance, and outcome in children with congenital heart disease. Br Heart J 59:480–485
Vincens JJ, Temizer D, Post JR, Edmunds LH Jr, Herrmann HC (1995) Long-term outcome of cardiac surgery in patients with mitral stenosis and severe pulmonary hypertension. Circulation 9(II):137–142
Yan C, Zhao S, Jiang S, Xu Z, Huang L, Zheng H, Ling J, Wang C, Wu W, Hu H, Zhang G, Ye Z, Wang H (2007) Transcatheter closure of patent ductus arteriosus with severe pulmonary arterial hypertension in adults. Heart 93:514–518
O’Donnell C, Ruygrok PN, Whyte K, Wilson NJ (2010) Progressive pulmonary hypertension post atrial septal defect device closure—early symptomatic improvement may not predict outcome. Heart Lung Circ 19:713–716
Schwerzmann M, Zafar M, McLaughlin PR, Chamberlain DW, Webb G, Granton J (2006) Atrial septal defect closure in a patient with “irreversible” pulmonary hypertensive arteriopathy. Int J Cardiol 110:104–107
Imanaka K, Kotsuka Y, Takamoto S, Furuse A, Inoue K, Shirai T (1998) Atrial septal defect and severe pulmonary hypertension in an adult who needed nitric oxide inhalation after repair. Kyobu Geka 51:403–405
Mizuhara A, Ino T, Adachi H, Ide H, Yamaguchi A, Kawahito K (1993) Surgical treatment of adult secundum ASD with severe pulmonary hypertension—two case reports. Nippon Kyobu Geka Gakkai Zasshi 41:1089–1093
Brooks D, Solway S, Gibbons WJ (2002) ATS statement: guidelines for the six-minute walk test. ATS Committee on Proficiency Standards for Clinical Pulmonary Function Laboratories. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 166:111–117
Sun WF, Dong ZF, Gong K, Zhang GP, Cui T, Xia YD, Dong J, Shen Y (2010) Transcatheter closure with use of the SHSMA occluder in 180 patients with congenital heart defects preliminary results. Tex Heart Inst J 37:531–537
Fujita H, Fukumoto Y, Saji K, Sugimura K, Demachi J, Nawata J, Shimokawa H (2010) Acute vasodilator effects of inhaled fasudil, a specific Rho-kinase inhibitor, in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension. Heart Vessels 25:144–149
Rimensberger PC, Spahr-Schopfer I, Berner M, Jaeggi E, Kalangos A, Friedli B, Beghetti M (2001) Inhaled nitric oxide versus aerosolized iloprost in secondary pulmonary hypertension in children with congenital heart disease: vasodilator capacity and cellular mechanisms. Circulation 103:544–548
Limsuwan A, Khosithseth A, Wanichkul S, Khowsathit P (2009) Aerosolized iloprost for pulmonary vasoreactivity testing in children with long-standing pulmonary hypertension related to congenital heart disease. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv 73:98–104
Berger M, Haimowitz A, Van Tosh A, Berdoff RL, Goldberg E (1985) Quantitative assessment of pulmonary hypertension in patients with tricuspid regurgitation using continuous wave Doppler ultrasound. J Am Coll Cardiol 6:359–365
McLaughlin VV, Archer SL, Badesch DB, Barst RJ, Farber HW, Lindner JR, Mathier MA, McGoon MD, Park MH, Rosenson RS, Rubin LJ, Tapson VF, Varga J, Harrington RA, Anderson JL, Bates ER, Bridges CR, Eisenberg MJ, Ferrari VA, Grines CL, Hlatky MA, Jacobs AK, Kaul S, Lichtenberg RC, Lindner JR, Moliterno DJ, Mukherjee D, Pohost GM, Rosenson RS, Schofield RS, Shubrooks SJ, Stein JH, Tracy CM, Weitz HH, Wesley DJ (2009) ACCF/AHA 2009 expert consensus document on pulmonary hypertension: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation taskforce on expert consensus documents and the American Heart Association. Circulation 119:2250–2294
Diller GP, Gatzoulis MA (2007) Pulmonary vascular disease in adults with congenital heart disease. Circulation 115:1039–1050
Galiè N, Torbicki A, Barst R, Dartevelle P, Haworth S, Higenbottam T, Olschewski H, Peacock A, Pietra G, Rubin LJ, Simonneau G (2004) Guidelines on diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension. Guidelines on diagnosis and treatment of PAH. The Task Force on Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur Heart J 25:2243–2278
Balint OH, Samman A, Haberer K, Tobe L, McLaughlin P, Siu SC, Horlick E, Granton J, Silversides CK (2008) Outcomes in patients with pulmonary hypertension undergoing percutaneous atrial septal defect closure. Heart 94:1189–1193
de Lezo JS, Medina A, Romero M, Pan M, Segura J, Caballero E, Pavlovic D, Ortega JR, Franco M, Delgado A, Ojeda S, Mesa D, Lafuente M (2002) Effectiveness of percutaneous device occlusion for atrial septal defect in adult patients with pulmonary hypertension. Am Heart J 144:877–880
Yong G, Khairy P, De Guise P, Dore A, Marcotte F, Mercier LA, Noble S, Ibrahim R (2009) Pulmonary arterial hypertension in patients with transcatheter closure of secundum atrial septal defects: a longitudinal study. Circ Cardiovasc Interv 2:455–462
Konstantinides S, Geibel A, Olschewski M, Görnandt L, Roskamm H, Spillner G, Just H, Kasper W (1995) A comparison of surgical and medical therapy for atrial septal defect in adults. N Engl J Med 333:469–473
Humenberger M, Rosenhek R, Gabriel H, Rader F, Heger M, Klaar U, Binder T, Probst P, Heinze G, Maurer G, Baumgartner H (2011) Benefit of atrial septal defect closure in adults: impact of age. Eur Heart J 32:553–560
Yock PG, Popp RL (1984) Noninvasive estimation of right ventricular systolic pressure by Doppler ultrasound in patients with tricuspid regurgitation. Circulation 70:657–662
Murata I, Kihara H, Shinohara S, Ito K (1992) Echocardiographic evaluation of pulmonary arterial hypertension in patients with progressive systemic sclerosis and related syndromes. Jpn Circ J 56:983–991
Shapiro SM, Oudiz RJ, Cao T, Romano MA, Beckmann XJ, Georgiou D, Mandayam S, Ginzton LE, Brundage BH (1997) Primary pulmonary hypertension: improved long-term effects and survival with continuous intravenous epoprostenol infusion. J Am Coll Cardiol 30:343–349
Jing ZC, Jiang X, Wu BX, Xu XQ, Wu Y, Ma CR, Wang Y, Yang YJ, Pu JL, Gao W (2009) Vardenafil treatment for patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension: a multicentre, open-label study. Heart 95:1531–1536
Chang SA, Jang SY, Ki CS, Kang IS, Kim DK (2011) Successful bosentan therapy for pulmonary arterial hypertension associated with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. Heart Vessels 26:231–234
Dimopoulos K, Inuzuka R, Goletto S, Giannakoulas G, Swan L, Wort SJ, Gatzoulis MA (2010) Improved survival among patients with Eisenmenger syndrome receiving advanced therapy for pulmonary arterial hypertension. Circulation 121:20–25
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Jing-xia Shen, Chun-hong Xiu, and Feng-hua Xue of the Department of Echocardiography in our hospital. Jing-xia Shen, director of Echocardiography, was in charge of monitoring for the process of interventional therapy. The follow-up of postclosure echocardiography was performed by Chun-hong Xiu and the echocardiographic data of the follow-up was recorded and sorted by Feng-hua Xue.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Z. Huang, Z. Fan and B. Wu contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, Zw., Fan, Zx., Sun, Jt. et al. The short- and medium-term results of transcatheter closure of atrial septal defect with severe pulmonary arterial hypertension. Heart Vessels 27, 603–609 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-011-0187-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-011-0187-4