Abstract
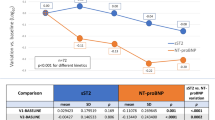
Systemic sclerosis (SSc) is characterized by vascular dysfunction that may lead to pulmonary artery hypertension (PAH). The N-terminal pro-B type natriuretic peptide (NT-proNBP), a marker of cardiac failure, is a diagnostic marker of early PAH in patients with SSc without heart failure. Our aim was to determine whether NT-proBNP levels may be a useful tool to evaluate the response to bosentan therapy in patients with PAH secondary to SSc. Ten patients with symptomatic, severe PAH secondary to SSc, received bosentan, 62.5 mg twice a day for 4 weeks followed by 125 mg twice a day for 7 months. Ten patients with SSc without PAH served as controls for basal level of NT-proBNP. Blood samples were obtained before the beginning of the therapy and after 3 and 7 months of treatment. SSc patients with PAH had significantly higher serum levels of NT-proBNP than those without PAH, at baseline. After 3 and 7 months of therapy, NT-proBNP concentration showed a progressive decrease, nearly approaching statistical difference at 7 months when compared to baseline levels (P = 0.953 and P = 0.600). Our results show that serum NT-proBNP levels may be a useful marker for the response to bosentan therapy in patients with PAH secondary to SSc.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siebold JR (2001) Scleroderma. In: Ruddy S, Harris ED, Sledge CB (eds) Kelley’s textbook of rheumatology, 6th edn. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 1211–1240
Allanore Y, Borderie D, Meune C, Cabanes L, Weber S, Ekindjian OG, Kahan A (2003) N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide as a diagnostic marker of early pulmonary artery hypertension in patients with systemic sclerosis and effects of calcium-channel blockers. Arthritis Rheum 48:3503–3508
Hobbs FD, Davis RC, Roalfe AK, Hare R, Davies MK, Kenkre JE (2002) Reliability of N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide assay in diagnosis of heart failure: cohort study in representative and high risk community populations. Br Med J 324:1498–1500
Greig D, Castro P, Ferrada M, Lim J, López C, Braun S, Córdova S, Salazar M (2006) Brain natriuretic peptide in primary pulmonary hypertension. Rev Med Chil 134:299–304
Mukerjee D, Yap LB, Holmes AM, Nair D, Ayrton P, Black CM, Coghlan JG (2003) Significance of plasma N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide in patients with systemic sclerosis-related pulmonary arterial hypertension. Respir Med 97:1230–1236
Williams MH, Handler CE, Akram R, Smith CJ, Das C, Smee J, Nair D, Denton CP, Black CM, Coghlan JG (2006) Role of N-terminal brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) in scleroderma-associated pulmonary arterial hypertension. Eur Heart J 27:1485–1494
Rubin LJ, Badesch DB, Barst RJ, Galie N, Black CM, Keogh A, Pulido T, Frost A, Roux S, Leconte I, Landzberg M, Simonneau G (2002) Bosentan therapy for pulmonary arterial hypertension. N Engl J Med 346:896–903
Karthikeyan VJ, Lip GY (2007) N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide and coronary artery disease. Eur J Clin Invest 37:18–25
Joglekar A, Tsai FS, McCloskey DA, Wilson JE, Seibold JR, Riley DJ (2006) Bosentan in pulmonary arterial hypertension secondary to sclerodermia. J Rheumatol 33:61–68
Cozzi F, Montisci R, Marotta H, Bobbo F, Durigon N, Ruscazio M, Sfriso P, Iliceto S, Todesco S (2006) Bosentan therapy of pulmonary arterial hypertension in connective tissue disease. Eur J Clin Invest 36:49–53
Williams MH, Das C, Handler CE, Akram MR, Davar J, Denton CP, Smith CJ, Black CM, Coghlan JG (2006) Systemic sclerosis associated pulmonary hypertension: improved survival in the current era. Heart 92:926–932
Souza R, Jardim C, Martins B, Cortopassi F, Yaksic M, Rabelo R, Bogossian H (2005) Effect of bosentan treatment on surrogate marker in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Curr Med Res Opin 21:907–911
Channick RN, Simonneau G, Sitbon O, Robbins IM, Frost A, Tapson VF, Badesch DB, Roux S, Rainisio M, Bodin F, Rubin LJ (2001) Effects of the dual endothelin-receptor antagonist bosentan in patients with pulmonary hypertension: a randomised placebo-controlled study. Lancet 358:1119–1123
Distler O, Pignone A (2006) Pulmonary arterial hypertension and rheumatic disease-from diagnosis to treatment. Rheumatology 45:22–25
Acknowledgment
We thank Dr. Nicola Martinelli for statistical analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Simeoni, S., Lippi, G., Puccetti, A. et al. N-terminal pro-BNP in sclerodermic patients on bosentan therapy for PAH. Rheumatol Int 28, 657–660 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-007-0510-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-007-0510-7