Abstract
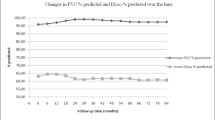
The purpose of the study was to examine prospectively the efficacy and safety of the combination of intravenous pulses of cyclophosphamide and methylprednizolone, in the treatment of scleroderma lung disease. Thirteen patients were treated with the above combination for up to 24 months. Prior to this treatment, they underwent a pulmonary function evaluation and high resolution computed tomography (HRCT). Carbon monoxide diffusion lung capacity and forced vital capacity were repeated at 6, 12, 24 and 48 months. HRCT was repeated at the end of the treatment period, but in between and afterwards in some patients, as well. A significant percentage of patients (66.6%) showed stabilization or improvement of their pulmonary function. Patients with already seriously compromised function, before treatment, were the least likely to exhibit this evolution pattern. There was a tendency in some individuals to deteriorate on later evaluations, off treatment, although they had stabilized at the end of the treatment. There was rather a poor correlation between functional evolution and HRCT appearance. Finally, the regimen was well tolerated. Our results suggest that the employed combination is safe and effective, mainly in stabilizing the respiratory function of the patients. This goal is more realistic when treatment is given before significant functional compromise has ensued. The need for long-term immunosuppression to maintain the initial favorable response is suggested.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Silver RM, Warrick JH, Kinsella MB, Staudt LS, Baumann MH, Strange C (1993) Cyclophosphamide and low-dose prednisone therapy in patients with systemic sclerosis (scleroderma) with interstitial lung disease. J Rheumatol 20:838–844
Steen VD, Lanz JK, Conte C, Owens GR, Medsger TA (1994) Therapy for severe interstitial lung disease in systemic sclerosis: a retrospective study. Arthritis Rheum 37:1290–1296
Akesson A., Scheja A, Lundin A, Wollheim F (1994) Improved pulmonary function in systemic sclerosis after treatment with cyclophosphamide. Arthritis Rheum 37:729–735
Clements P, Furst DE, Silver RM, Tashkin DP, Roth MD, Goldin J, Elashoff RM,Sterz MG, for the SLS Investigators (2005) The Scleroderma Lung Study (SLS) shows the beneficial effects of cyclophosphamide over placebo in systemic sclerosis patients with active alveolitis. Arthritis Rheum 52(Suppl:s257)
Schnabel A, Reuter M, Gross WL (1998) Ιntravenous pulse cyclophosphamide in the treatment of interstitial lung disease due to collagen vascular disease. Arthritis Rheum 41:1215–1220
Davas EM, Peppas C, Maragou M, Alvanou E, Hondros D, Dantis PC (1999) Intravenous cyclophosphamide pulse therapy for the treatment of lung disease associated with scleroderma. Clin Rheumatol 18:455–461
Varai G, Earle L, Jimenez SA, Steiner RM, Varga J (1998) A pilot study of intermittent intravenous cyclophosphamide for the treatment of systemic sclerosis associated lung disease. J Rheumatol 25:1325–1329
Pakas I, Ioannidis JP, Malagari K, Skopouli FN, Moutsopoulos HM, Vlachoyiannopoulos PG (2002) Cyclophosphamide with low or high dose prednisolone for systemic sclerosis lung disease. J Rheumatol 29:298–304
Giacomelli R, Valentini G, Salsano F, Cipriani P, Sambo P, Conforti ML, Fulminis A, De Luca A, Farina G, Candela M, Generini S, De Francisci A, Tirri E, Proietti M,Bombardieri S, Gabrielli A, Tonietti G, Gerinic MM (2002) Cyclophosphamide pulse regimen in the treatment of alveolitis in systemic sclerosis. J Rheumatol 29:721–736
Griffiths B, Miles S, Moss H, Robertson R, Veale D, Emery P (2002) Systemic sclerosis and interstitial lung disease: a pilot study using pulse intravenous methylprednisolone and cyclophosphamide to assess the effect on high resolution computed tomography scan and lung function. J Rheumatol 29:2371–2378
Airò P, Danieli E, Parrinello G, Antonioli CM, Cavazzana I, Toniati P, Franceschini F, Cattaneo R (2004) Intravenous cyclophosphamide therapy for systemic sclerosis. A single-center experience and review of the literature with pooled analysis of lung function test results. Clin Exp Rheumatol 22:573–578
Kowal-Bielecka O, Kowal K, Rojewska J, Bodzenta-Lukaszyk A, Siergiejko M, Sierakowska M, Sierakowski S (2005) Cyclophosphamide reduces neutrophilic alveolitis in patients with scleroderma lung disease: a retrospective analysis of serial bronchoalveolar lavage investigations. Ann Rheum Dis 64:1343–1346
Warrick JH, Bhalla M, Schabel SI, Silver RM (1991) High resolution computed tomography in early scleroderma lung disease. J Rheumatol 18:1520–1528
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yiannopoulos, G., Pastromas, V., Antonopoulos, I. et al. Combination of intravenous pulses of cyclophosphamide and methylprednizolone in patients with systemic sclerosis and interstitial lung disease. Rheumatol Int 27, 357–361 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-006-0217-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-006-0217-1