Abstract
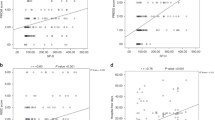
Surfactant-associated protein (SP-A) was measured in tracheal aspirates of ventilated infants with (n=51) and without (n=21) respiratory distress syndrome (RDS). SP-A concentrations in samples collected after birth were significantly lower in RDS than in infants ventilated for other reasons than RDS (median 0.03 vs. 1.60 μg/ml). As a biochemical test to diagnose RDS early after birth, the sensitivity of measuring SP-A in tracheal aspirates was 87% and specificity 81%. SP-A content in tracheal aspirates of infants with RDS was monitored during the first 7 days of life. A significant (P<0.001) increase within the first 4 days was found in those infants who survived, whereas no such change was found in those infants who died.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SP-A:
-
surfactant-associated protein A
- RDS:
-
respiratory distress syndrome
References
Bartlett GR (1959) Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem 234:466–468
Bligh EG, Dyer WJ (1959) A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol 37:911–917
Chida S, Phelps D, Cordle C, Soll R, Floros J, Taeusch HW (1988) Surfactant-associated proteins in tracheal aspirates of infants with respiratory distress syndrome after surfactant therapy. Am Rev Respir Dis 137:943–947
Collaborative European Multicenter Study Group (1989) Surfactant replacement therapy for severe neonatal respiratory distress syndrome: an international randomized clinical trial. Pediatrics 82:683–691
Francoual J, Magny JF, Ropert JC, Dehan M, Leluc R (1987) Phosphatidylglycerol in tracheal aspirates for diagnosis of hyaline membrane disease. Arch Dis Child 62:193–194
Gerdes JS, Abbasi S, Karp K, Hull W, Whitsett JA (1990) Surfactant protein-A in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid from neonates with RDS on conventional and high-frequency oscillatory ventilation. Pediatr Pulmonol 9:166–169
Gikas EG, King RJ, Mescher EJ, Platzker ACG, Kitterman JA, Ballard PL, Benson BJ, Tooley WH, Tooley WH, Clements JA (1977) Radioimmunoassay of pulmonary surface-active material in the tracheal fluid of the fetal lamb. Am Rev Respir Dis 115:587–593
Hallman M, Arjomaa P, Mizumoto M, Akino T (1988) Surfactant proteins in the diagnosis of fetal lung maturity. 1. Predictive accuracy of the 35 kD protein, the lecithin/sphingomyelin ratio, and phosphatidylglycerol. Am J Obstet Gynecol 158:531–535
Hjalmarson O (1981) Epidemiology and classification of acute, neonatal respiratory disorders. Acta Paediatr Scand 70:773–783
Kattner E, Maier R, Waiß E, Stevens P (1990) Lecithin/sphingomyelin ratio from tracheal aspirates and compliance of the respiratory system in infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Lung [Suppl]:883–890
Katyal SL, Amenta JS, Singh G, Silverman JA (1984) Deficient lung surfactant apoproteins in amniotic fluid with mature phospholipid profile from diabetic pregnancies. Am J Obstet Gynecol 148:48–53
Katyal SL, Singh G (1983) An enzyme-linked immunoassay of surfactant apoproteins. Its application to the study of fetal lung development in the rat. Pediatr Res 17:439–443
King RJ, Ruch J, Gikas EG, Platzker ACG, Creasy RK (1975) Appearance of apoproteins of pulmonary surfactant in human amniotic fluid. J Appl Physiol 39:735–741
Kuroki Y, Takahashi H, Fukada Y, Mikawa M, Inagawa A, Fujimito S, Akino T (1985) Two-site “simultaneous” immunoassay with monoclonal antibodies for the determination of surfactant apoproteins in human amniotic fluid. Pediatr Res 19:1017–1020
Lotze A, Whitsett JA, Kammerman JA, Ritter M, Taylor GA, Short BL (1990) Surfactant protein A concentrations in tracheal aspirate fluid from infants requiring extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. J Pediatr 116:435–440
deMello DE, Phelps DS, Patel G, Floros J, Lagunoff D (1989) Expression of the 35 kDa and low molecular weight surfactant-associated proteins in the lungs of infants dying with respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Pathol 134:1285–1293
Merritt TA, Hallman M (1988) Surfactant replacement. A new era with many challenges for neonatal medicine. Am J Dis Child 142:1333–1339
Nogee LM, Wispé JR (1988) Effects of pulmonary oxygen injury on airway content of surfactant-associated protein A. Pediatr Res 24:568–573
Nogee LM, Wispé JR, Clark JC, Whitsett JA (1989) Increased synthesis and mRNA of surfactant protein A in oxygen-exposed rats. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 1:119–125
Obladen M, Gluck L (1977) Tracheale Phospholipide beim Atemnotsyndrom des Neugeborenen. Monatsschr Kinderheilkd 125:431–433
Segerer H, Stevens P, Schadow B, Maier R, Kattner E, Schwarz H, Curstedt T, Robertson B, Obladen M (1991) Surfactant substitution in ventilated very low birth weight infants: factors related to response types. Pediatr Res 30:591–596
Shelley SA, Balis JU, Paciga JE, Knuppel RA, Ruffolo EH, Bouis PJ (1982) Surfactant “apoproteins” in human amniotic fluid: an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the prenatal assessment of lung maturity. Am J Obstet Gynecol 144:224–228
Wright JR, Clements JA (1987) Metabolism and turnover of lung surfactant. Am Rev Respir Dis 135:426–444
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The contributions of the first two authors should be considered equal
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stevens, P.A., Schadow, B., Bartholain, S. et al. Surfactant protein A in the course of respiratory distress syndrome. Eur J Pediatr 151, 596–600 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01957730
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01957730