Abstract
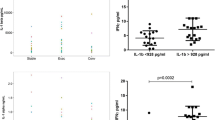
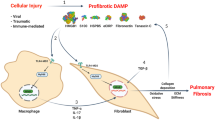
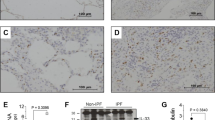
Severe forms of idiopathic interstitial pneumonia (IIP), such as usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP), can be impervious to modern steroid and immunosuppressive treatment regimens, thereby emphasizing the need for novel effective therapies. Understanding the cytokine networks that may affect immune and structural cell activation and, hence, the progression of these fatal fibrotic diseases, has been a focus in our research. In this regard, we have examined the role of interleukin (IL)-4 and IL-13 and their respective receptor subunits in this process. Examination of clinical surgical lung biopsies (SLBs) showed that IIP is characterized by the abnormal, heightened expression of the receptor subunits that bind IL-4 and IL-13. Specifically, IL-4Rα and IL-13Rα2 (the high-affinity IL-13 receptor subunit) was present in greater abundance in SLBs and fibroblasts from IIP patients compared with normal patients, who exhibited no evidence of pulmonary fibrosis. These clinical findings prompted us to investigate whether the targeting of pulmonary cell types that were highly responsive to IL-4 and IL-13 was a viable therapeutic option in IIP. Using a chimeric protein comprised of human IL-13 and a truncated version of an exotoxin from Pseudomonas (abbreviated IL13-PE), we observed that IL13-PE selectively targeted human pulmonary fibroblasts grown from IIP SLBs, whereas it had a minimal effect on fibroblasts grown from biopsies from normal patients. In murine models characterized by abnormal airway or interstitial fibrotic responses, the intranasal administration of IL13-PE significantly attenuated the fibrotic response through the targeting of IL-4Rα-and IL-13Rα2-expressing pulmonary cells, including monocytes, macrophages, and pulmonary fibroblasts. Together, these data demonstrate that IL-4 and IL-13 are required for the initiation and maintenance of pulmonary fibrosis, and highlight the importance of further investigation of anti-fibrotic therapeutics that prevent the action of both cytokines during clinical pulmonary fibrosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Green FH: Overview of pulmonary fibrosis. Chest 2002;122:334S-339S.
Travis W, Matsui K, Moss J, Ferrans V: Idiopathic nonspecific interstitial pneumonia: Prognostic significance of cellular and fibrosing patterns. Am J Surg Path 2000;24:19–33.
Katzenstein A, Myers J: Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Clinical relevance of pathologic classification. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1998;157:1301–1315.
Myers JL: NSIP, UIP, and the ABCs of idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. Eur Respir J 1998;12:1003–1004.
American Thoracic Society, European Respiratory Society (ATS/ERS) international multidisciplinary consensus classification of idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2002;165:277–304.
Nagai S, Kitaichi M, Itoh H, Nishimura K, Colby T: Idiopathic nonspecific interstitial pneumonia/fibrosis: comparison with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and BOOP. Eur Respir J 1998;12:1010–1019.
Daniil Z, Gilchrist F, Nicholson A, Hansell D, Harris J, Colby T, duBois R: A histologic pattern of nonspecific interstitial pneumonia is associated with a better prognosis than usual interstitial pneumonia in patients with cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1999;160:899–905.
Hampton J, Martinez F, Orens J, Toews G, Lynch III J: Corticosteroids in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF): toxicity may outweight benefits. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1994;149:A878.
Flaherty KR, Toews GB, Travis WD, Colby TV, Kazerooni EA, Gross BH, et al.: Clinical significance of histological classification of idiopathic interstitial pneumonia. Eur Respir J 2002;19:275–283.
Lasky JA, Brody AR: Interstitial fibrosis and growth factors. Environ Health Perspect 2000;108 Suppl 4:751–762.
Allen JT, Spiteri MA: Growth factors in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: relative roles. Respir Res 2002;3:13.
Coker RK, Laurent GJ: Pulmonary fibrosis: cytokines in the balance. Eur Respir J 1998;11:1218–1221.
Wallace WA, Ramage EA, Lamb D, Howie SE: A type 2 (Th2-like) pattern of immune response predominates in the pulmonary interstitium of patients with cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis (CFA). Clin Exp Immunol 1995;101:436–441.
Wallace WA, Howie SE: Immunoreactive interleukin 4 and interferon-gamma expression by type II alveolar epithelial cells in interstitial lung disease. J Pathol 1999;187:475–480.
Lukacs NW, Hogaboam C, Chensue SW, Blease K, Kunkel SL: Type 1/type 2 cytokine paradigm and the progression of pulmonary fibrosis. Chest 2001;120:5S-8S.
Gurujeyalakshmi G, Giri SN: Molecular mechanisms of anti-fibrotic effect of interferon gamma in bleomycinmouse model of lung fibrosis: down regulation of TGF-beta and procollagen I and III gene expression. Exp Lung Res 1995;21:791–808.
Segel MJ, Cohen PY, Izbicki G, Or R, Christensen TG, Wallach-Dayan SB, Breuer R: The role of interferon-{gamma} in the evolution of murine bleomycin lung fibrosis. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2003
Ziesche R, Hofbauer E, Wittmann K, Petkov V, Block L: A preliminary study of long-term treatment with interferon gamma-1b and low-dose prednisone in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N Engl J Med 1999;341:1264–1269.
Prasse A, Muller KM, Kurz C, Hamm H, Virchow JC, Jr.: Does interferon-gamma improve pulmonary function in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis? Eur Respir J 2003;22:906–911.
Raghu G, Brown KK, Bradford WZ, Starko K, Noble PW, Schwartz DA, King TE, Jr.: A placebo-controlled trial of interferon gamma-1b in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N Engl J Med 2004;350:125–133.
Postlethwaite AE, Holness MA, Katai H, Raghow R: Human fibroblasts synthesize elevated levels of extracellular matrix proteins in response to interleukin-4. J Clin Invest 1992;90:1479–1485.
Gharaee-Kermani M, Denholm EM, Phan SH: Costimulation of fibroblast collagen and transforming growth factor betal gene expression by monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 via specific receptors. J Biol Chem 1996;271:17779–17784.
Hogaboam CM, Bone-Larson CL, Lipinski S, Lukacs NW, Chensue SW, Strieter RM, Kunkel SL. Differential monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 and chemokine receptor 2 expression by murine lung fibroblasts derived from Th1- and Th2-type pulmonary granuloma models. J Immunol 1999;163:2193–2201.
Makhluf HA, Stepniakowska J, Hoffman S, Smith E, LeRoy EC, Trojanowska M. IL-4 upregulates tenascin synthesis in scleroderma and healthy skin fibroblasts. J Invest Dermatol 1996;107:856–859.
Postlethwaite AE, Seyer JM: Fibroblast chemotaxis induction by human recombinant interleukin-4. Identification by synthetic peptide analysis of two chemotactic domains residing in amino acid sequences 70–88 and 89–122. J Clin Invest 1991;87:2147–2152.
Jakubzick C, Choi ES, Kunkel SL, Joshi BH, Puri RK, Hogaboam CM. Impact of interleukin-13 responsiveness on the synthetic and proliferative properties of Th1-and Th2-type pulmonary granuloma fibroblasts. Am J Pathol 2003;162:1475–1486.
Zhu Z, Ma B, Zheng T, Homer RJ, Lee CG, Charo IF, et al.: IL-13-induced chemokine responses in the lung: role of CCR2 in the pathogenesis of IL-13-induced inflammation and remodeling. J Immunol 2002;168:2953–2462.
Moore BB, Paine R, 3rd, Christensen PJ, Moore TA, Sitterding S, Ngan R, et al.: Protection from pulmonary fibrosis in the absence of CCR2 signaling. J Immunol 2001;167:4368–4377.
Belperio JA, Dy M, Burdick MD, Xue YY, Li K, Elias JA, Keane MP. Interaction of IL-13 and C10 in the pathogenesis of bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2002;27:419–427.
Doucet C, Brouty-Boye D, Pottin-Clemenceau C, Canonica GW, Jasmin C, Azzarone B: Interleukin (IL) 4 and IL-13 act on human lung fibroblasts. Implication in asthma. J Clin Invest 1998;101:2129–2139.
Doucet C, Brouty-Boye D, Pottin-Clemenceau C, Jasmin C, Canonica GW, Azzarone B: IL-4 and IL-13 specifically increase adhesion molecule and inflammatory cytokine expression in human lung fibroblasts. Int Immunol 1998;10:1421–1433.
Sempowski GD, Beckmann MP, Derdak S, Phipps RP: Subsets of murine lung fibroblasts express membrane-bound and soluble IL-4 receptors. Role of IL-4 in enhancing fibroblast proliferation and collagen synthesis. J Immunol 1994;152:3606–3614.
Zhu Z, Homer RJ, Wang Z, Chen Q, Geba GP, Wang J, et al.: Pulmonary expression of interleukin-13 causes inflammation, mucus hypersecretion, subepithelial fibrosis, physiologic abnormalities, and eotaxin production. J Clin Invest 1999;103:779–788.
Lee CG, Homer RJ, Zhu Z, Lanone S, Wang X, Koteliansky V, et al.: Interleukin-13 induces tissue fibrosis by selectively stimulating and activating transforming growth factor beta(1). J Exp Med 2001;194:809–821.
Blease K, Jakubzick C, Westwick J, Lukacs N, Kunkel SL, Hogaboam CM: Therapeutic effect of IL-13 immunoneutralization during chronic experimental fungal asthma. J Immunol 2001;166:5219–5224.
Blease K, Jakubzick C, Schuh JM, Joshi BH, Puri RK, Hogaboam CM: IL-13 fusion cytotoxin ameliorates chronic fungal-induced allergic airway disease in mice. J Immunol 2001;167:6583–6592.
Chiaramonte MG, Donaldson DD, Cheever AW, Wynn TA: An IL-13 inhibitor blocks the development of hepatic fibrosis during a T-helper type 2-dominated inflammatory response. J Clin Invest 1999;104:777–785.
Chiaramonte MG, Cheever AW, Malley JD, Donaldson DD, Wynn TA: Studies of murine schistosomiasis reveal interleukin-13 blockade as a treatment for established and progressive liver fibrosis. Hepatology 2001;34:273–282.
Lee JH, Kaminski N, Dolganov G, Grunig G, Koth L, Solomon C, et al.: Interleukin-13 induces dramatically different transcriptional programs in three human airway cell types. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2001;25:474–485.
Homer RJ, Zheng T, Chupp G, He S, Zhu Z, Chen Q, et al.: Pulmonary type II cell hypertrophy and pulmonary lipoproteinosis are features of chronic IL-13 exposure. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2002;283:L52-L59.
Hancock A, Armstrong L, Gama R, Millar A: Production of interleukin 13 by alveolar macrophages from normal and fibrotic lung. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 1998;18;60–65.
Oriente A, Fedarko NS, Pacocha SE, Huang SK, Lichtenstein LM, Essayan DM: Interleukin-13 modulates collagen homeostasis in human skin and keloid fibroblasts. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2000;292:988–994.
Richter A, Puddicombe SM, Lordan JL, Bucchieri F, Wilson SJ, Djukanovic R, et al.: The contribution of interleukin (IL)-4 and IL-13 to the epithelial-mesenchymal trophic unit in asthma. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2001;25:385–391.
Wynn TA: IL-13 effector functions. Annu Rev Immunol 2003;21:425–456.
Chiaramonte MG, Mentink-Kane M, Jacobson BA, Cheever AW, Whitters MJ, Goad ME, et al.: Regulation and function of the interleukin 13 receptor alpha 2 during a T helper cell type 2-dominant immune response. J Exp Med 2003;197:687–701.
Wood N, Whitters MJ, Jacobson BA, Witek J, Sypek JP, Kasaian M, et al.: Enhanced interleukin (IL)-13 responses in mice lacking IL-13 receptor alpha 2. J Exp Med 2003;197:703–709.
Mentink-Kane MM, Cheever AW, Thompson RW, Hari DM, Kabatereine NB, Vennervald BJ, et al.: IL-13 receptor {alpha} 2 down-modulates granulomatous inflammation and prolongs host survival in schistosomiasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004;101:586–590.
Kawakami K, Taguchi J, Murata T, Puri RK: The interleukin-13 receptor alpha2 chain: an essential component for binding and internalization but not for interleukin-13-induced signal transduction through the STAT6 pathway. Blood 2001;97:2673–2679.
Toru H, Pawankar R, Ra C, Yata J, Nakahata T: Human mast cells produce IL-13 by high-affinity IgE receptor cross-linking: enhanced IL-13 production by IL-4-primed human mast cells. J Allergy Clin Immunol 1998;102:491–502.
Murata T, Obiri NI, Debinski W, Puri RK: Structure of IL-13 receptor: analysis of subunit composition in cancer and immune cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1997;238:90–94.
Murata T, Husain SR, Mohri H, Puri PK: Two different IL-13 receptor chains are expressed in normal human skin fibroblasts, and IL-4 and IL-13 mediate signal transduction through a common pathway. Int Immunol 1998;10:1103–1110.
McKenzie AN, Culpepper JA, de Waal Malefyt R, Briere F, Punnonen J, Aversa G, et al.: Interleukin 13, a T-cell-derived cytokine that regulates human monocyte and B-cell function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1993;90:3735–3739.
McKenzie AN: Regulation of T helper type 2 cell immunity by interleukin-4 and interleukin-13. Pharmacol Ther 2000;88:143–151.
Bochner BS, Klunk DA, Sterbinsky SA, Coffman RL, Schleimer RP. IL-13 selectively induces vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 expression in human endothelial cells. J Immunol 1995;154:799–803.
Zheng T, Zhu Z, Liu W, Lee CG, Chen Q, Homer RJ, Elias JA: Cytokine regulation of IL-13Ralpha2 and IL-13Ralpha1 in vivo and in vitro. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2003;111:720–728.
Kawakami K, Kawakami M, Joshi BH, Puri PK: Interleukin-13 receptor-targeted cancer therapy in an immunodeficient animal model of human head and neck cancer. Cancer Res 2001;61:6194–6200.
Kawakami M, Kawakami K, Puri RK: Apoptotic pathways of cell death induced by an interleukin-13 receptortargeted recombinant cytotoxin in head and neck cancer cells. Cancer Immunol Immunother 2002;50:691–700.
Hogaboam CM, Steinhauser ML, Chensue SW, Kunkel SL: Novel roles for chemokines and fibroblasts in interstitial fibrosis. Kidney Int 1998;54:2152–2159.
Selman M, Pardo A: Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: an epithelial/fibroblastic cross-talk disorder. Respir Res 2002;3:3.
Lynch JP, 3rd, White E, Flaherty K: Corticosteroids in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Curr Opin Pulm Med 2001;7:298–308.
Flaherty KR, Toews GB, Lynch JP, 3rd, Kazerooni EA, Gross BH, Strawderman RL, et al.: Steroids in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a prospective assessment of adverse reactions, response to therapy, and survival. Am J Med 2001;110:278–282.
Gauldie J, Kolb M, Sime PJ: A new direction in the pathogenesis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis? Respir Res 2002;3:1.
van den Blink B, Jansen HM, Peppelenbosch MP: Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: molecular mechanisms and possible therapeutic strategies. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz) 2000;48:539–545.
Gharaee-Kermani M, Nozaki Y, Hatano K, Phan SH: Lung interleukin-4 gene expression in a murine model of bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Cytokine 2001;15:138–147.
King TE, Jr., Schwarz MI, Brown K, Tooze JA, Colby TV, Waldron JA, et al.: Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: relationship between histopathologic features and mortality. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2001;164:1025–1032.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jakubzick, C., Kunkel, S.L., Puri, R.K. et al. Therapeutic targeting of IL-4-and IL-13-responsive cells in pulmonary fibrosis. Immunol Res 30, 339–349 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1385/IR:30:3:339
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/IR:30:3:339