Abstract
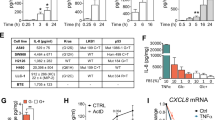
Malignant pleural effusion (MPE) is a poor prognostic sign for patients with non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). The generation of MPE is largely regulated by vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), and upregulation of VEGF by Stat3 has been observed in several types of tumor cells. In this study, we demonstrate constitutively activated Stat3 in several human lung cancer cell lines and in tumor cells infiltrated in the pleurae of patients with adenocarcinoma cell lung cancer (ADCLC) and MPE. The observations suggest that activated Stat3 plays a role in the pathogenesis of ADCLC. In PC14PE6/AS2 cells, a Stat3-positive human ADCLC cell line, autocrine IL-6 activated Stat3 via JAKs, not via Src kinase. PC14PE6/AS2 cells express higher VEGF mRNA and protein than do Stat3-negative PC14PE6/AS2/dnStat3 cells. In an animal model, PC14P6/AS2/dnStat3 cells produced no MPE and less lung metastasis than did PC14P6/AS2 cells. PC14PE6/AS2 cells also expressed higher VEGF protein, microvessel density, and vascular permeability in tumors than did PC14P6/AS2/dnStat3 cells. Therefore, we hypothesize that autocrine IL-6 activation of Stat3 in ADCLC may be involved in the formation of malignant pleural effusion by upregulating VEGF. Higher levels of IL-6 and VEGF were also found in the pleural fluids of patients with ADCLC than in patients with congestive heart failure. The autocrine IL-6/Stat3/VEGF signaling pathway may also be activated in patients with ADCLC and MPE. These findings provide novel targets for the management of MPE.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexandrakis MG, Coulocheri SA, Bouros D, Mandalaki K, Karkavitsas N, Eliopoulos GD . (2000). Oncol Rep 7: 1327–1332.
Anderson CB, Philpott GW, Ferguson TB . (1974). Cancer 33: 916–922.
Bihl M, Tamm M, Nauck M, Wieland H, Perruchoud AP, Roth M . (1998). Am J Resp Cell Mol Biol 19: 606–612.
Bromberg JF, Wrzeszczynska MH, Devgan G, Zhao Y, Pestell RG, Albanese C et al. (1999). Cell 98: 295–303.
Buettner R, Mora LB, Jove R . (2002). Clin Cancer Res 8: 945–954.
Carmeliet P, Ferreira V, Breier G, Pollefeyt S, Kieckens L, Gertsenstein M et al. (1996). Nature 380: 435–439.
Dvorak HF, Brown LF, Detmar M, Dvorak AM . (1995). Am J Pathol 146: 1029–1039.
Fernandes A, Hamburger AW, Gerwin BI . (1999). Int J Cancer 83: 564–570.
Ferrara N, Carver-Moore K, Chen H, Dowd M, Lu L, O'Shea KS et al. (1996). Nature 380: 439–442.
Hoffman PC, Mauer AM, Vokes EE . (2000). Lancet 355: 479–485.
Hoheisel G, Izbicki G, Roth M, Chan CH, Reichenberger F, Schauer J et al. (1998). Respiration 65: 183–186.
Hung TL, Chen FF, Liu JM, Lai WW, Hsiao AL, Huang WT et al. (2003). Clin Cancer Res 9: 2605–2612.
Hutchins D, Steel CM . (1994). Int J Cancer 58: 80–84.
Kishimoto T, Akira S, Taga T . (1992). Science 258: 593–597.
Levy DE, Darnell Jr JE . (2002). Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3: 651–662.
Memon A, Zawadzki ZA . (1981). Curr Probl Cancer 5: 1–30.
Mesiano S, Ferrara N, Jaffe RB . (1998). Am J Pathol 153: 1249–1256.
Naito T, Satoh H, Ishikawa H, Yamashita YT, Kamma H, Takahashi H et al. (1997). Anticancer Res 17: 4743–4746.
Nakajima K, Yamanaka Y, Nakae K, Kojima H, Ichiba M, Kiuchi N et al. (1996). EMBO J 15: 3651–3658.
Niu G, Wright KL, Huang M, Song L, Haura E, Turkson J et al. (2002). Oncogene 21: 2000–2008.
Okamoto M, Lee C, Oyasu R . (1997). Cancer Res 57: 141–146.
Seki Y, Suzuki N, Imaizumi M, Iwamoto T, Usami N, Ueda Y et al. (2004). Int J Oncol 24: 931–934.
Senger DR, Galli SJ, Dvorak AM, Perruzzi CA, Harvey VS, Dvorak HF . (1983). Science 219: 983–985.
Siegsmund MJ, Yamazaki H, Pastan I . (1994). J Urol 151: 1396–1399.
Song L, Turkson J, Karras JG, Jove R, Haura EB . (2003). Oncogene 22: 4150–4165.
Sugiura S, Ando Y, Minami H, Ando M, Sakai S, Shimokata K . (1997). Clin Cancer Res 3: 47–50.
Takayama K, Ueno H, Nakanishi Y, Sakamoto T, Inoue K, Shimizu K et al. (2000). Cancer Res 60: 2169–2177.
Turkson J . (2004). Expert Opin Ther Targets 8: 409–422.
Wei LH, Kuo ML, Chen CA, Chou CH, Lai KB, Lee CN et al. (2003). Oncogene 22: 1517–1527.
Wells J, Boyd KE, Fry CJ, Bartley SM, Farnham PJ . (2000). Mol Cell Biol 20: 5797–5807.
Yamaguchi T, Kimura H, Yokota S, Yamamoto Y, Hashimoto T, Nakagawa M et al. (2000). Jpn J Clin Oncol 30: 53–58.
Yano S, Herbst RS, Shinohara H, Knighton B, Bucana CD, Killion JJ et al. (2000a). Clin Cancer Res 6: 957–965.
Yano S, Shinohara H, Herbst RS, Kuniyasu H, Bucana CD, Ellis LM et al. (2000b). Am J Pathol 157: 1893–1903.
Yokoyama A, Maruyama M, Ito M, Kohno N, Hiwada K, Yano S . (1992). Chest 102: 1055–1059.
Yu H, Jove R . (2004). Nat Rev Cancer 4: 97–105.
Zebrowski BK, Yano S, Liu W, Shaheen RM, Hicklin DJ, Putnam Jr JB et al. (1999). Clin Cancer Res 5: 3364–3368.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants 91-B-FA09-1-4 from the Ministry of Education Program to Promote Academic Excellence in Universities, and NSC 93-2314-B-006-035.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc).
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yeh, HH., Lai, WW., Chen, H. et al. Autocrine IL-6-induced Stat3 activation contributes to the pathogenesis of lung adenocarcinoma and malignant pleural effusion. Oncogene 25, 4300–4309 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209464
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209464
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Malignant pleural effusion: current understanding and therapeutic approach
Respiratory Research (2024)
-
Systematic analysis of IL-6 as a predictive biomarker and desensitizer of immunotherapy responses in patients with non-small cell lung cancer
BMC Medicine (2022)
-
BMP2 promotes lung adenocarcinoma metastasis through BMP receptor 2-mediated SMAD1/5 activation
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Th17 cells and their related cytokines: vital players in progression of malignant pleural effusion
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2022)
-
The intersection of COVID-19 and cancer: signaling pathways and treatment implications
Molecular Cancer (2021)