Abstract
Purpose
Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSAS) is highly prevalent in the elderly. Unattended, at-home portable monitoring (PM) is a diagnostic alternative to polysomnography in adults with high clinical probability of OSAS. However, no studies have evaluated the diagnostic accuracy of PM in elderly population. The aim of our study was to evaluate the effectiveness of PM in elderly patients.
Methods
We selected patients aged over 65 years with suspected OSAS. Two-order randomized evaluations were performed: one night of at-home PM (PMhome) and one night of simultaneous PM and polysomnography (PSG) in the sleep lab (PSG+PM). We obtained three different apnea–hypopnea index (AHI): AHI from PSG (AHI PSG), AHI from at-home PM (AHI PMhome), and AHI from PM+PSG (AHI PM+PSG). Two technicians, blinded to the recording order, scored each sleep study.
Results
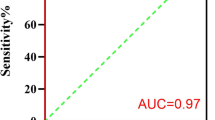
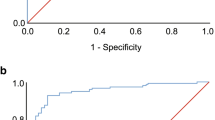
We studied a total of 43 patients. No difference between the AHI values for each of the different recordings was found (p > 0.05). There was good correlation between AHI PSG and AHI PMhome (r = 0.67) and AHI PSG+PM (r = 0.84). The area under the receiver operator curve was above 0.83, indicating good sensitivity and a positive predictive value for AHI with cutoffs of 5, 15, and 30 and good specificity and negative predictive value for AHI values above 15. Correlation, accuracy, and agreement were greater when the recordings were made simultaneously.
Conclusions
PM was effective for diagnosing OSAS in the elderly and can be used as an alternative to PSG in elderly patients with a high clinical probability of OSAS.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bliwise DL (2009) Epidemiology of age-dependence in sleep disordered breathing (SDB) in old age: the bay area sleep cohort (basc). Sleep Med Clin 4:57–64
Phillips BA, Berry DT, Lipke-Molby TC (1996) Sleep-disordered breathing in healthy aged persons. Fifth and final year follow-up. Chest 110:654–658
Phillips BA, Ancoli-Israel S (2001) Sleep disorders in the elderly. Sleep Med 2:99–114
Ancoli-Israel S, Kripke DF, Klauber MR, Mason WJ, Fell R, Kaplan O (1991) Sleep-disordered breathing in community-dwelling elderly. Sleep 14:486–495
Bixler EO, Vgontzas AN, Ten Have T, Tyson K, Kales A (1998) Effects of age on sleep apnea in men: I. Prevalence and severity. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 157:144–148
Bixler EO, Vgontzas AN, Lin HM, Ten Have T, Rein J, Vela-Bueno A, Kales A (2001) Prevalence of sleep-disordered breathing in women: effects of gender. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 163:608–613
Durán J, Esnaola S, Rubio R, Iztueta A (2001) Obstructive sleep apnea-hypopnea and related clinical features in a population-based sample of subjects aged 30 to 70 year. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 163:685–689
Young T, Shahar E, Nieto FJ, Redline S, Newman AB, Gottlieb DJ, Walsleben JA, Finn L, Enright P, Samet JM, Sleep Heart Health Study Research Group (2002) Predictors of sleep-disordered breathing in community-dwelling adults: the Sleep Heart Health Study. Arch Intern Med 162:893–900
Punjabi NM, Caffo BS, Goodwin JL, Gottlieb DJ, Newman AB, O’Connor GT, Rapoport DM, Redline S, Resnick HE, Robbins JA, Shahar E, Unruh ML, Samet JM (2009) Sleep-disordered breathing and mortality: a prospective cohort study. PLoS Med 6:e1000132
Carskadon MA, Dement WC (1981) Respiration during sleep in the aged human. J Gerontol 36:420–423
Coleman RM, Miles LE, Guilleminault CC, Zarcone VP Jr, van den Hoed J, Dement WC (1981) Sleep-wake disorders in the elderly: polysomnographic analysis. J Am Geriatr Soc 29:289–296
Roehrs T, Zorick F, Sicklesteel J, Wittig R, Roth T (1983) Age-related sleep-wake disorders at a sleep disorder center. J Am Geriatr Soc 31:364–370
Yesavage J, Bliwise D, Guilleminault C, Carskadon M, Dement W (1985) Preliminary communication: intellectual deficit and sleep-related respiratory disturbance in the elderly. Sleep 8:30–33
Ancoli-Israel S, Kripke DF, Mason W, Kaplan OJ (1985) Sleep apnea and periodic movements in an aging sample. J Gerontol 40:419–425
Mosko SS, Dickel MJ, Paul T, LaTour T, Dhillon S, Ghanim A, Sassin JF (1988) Sleep apnea and sleep-related periodic leg movements in community resident seniors. J Am Geriatr Soc 36:502–508
Tufik S, Santos-Silva R, Taddei J, Bittencourt LA (2010) Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome in the Sao Paulo Epidemiologic Sleep Study. Sleep Med 11:441–446
American Sleep Disorders Association (1994) Practice parameters for the use of portable recording in the assessment of obstructive sleep apnea. Standards of Practice Committee of the American Sleep Disorders Association. Sleep 17:372–377
Collop NA, Anderson WM, Boehlecke B, Claman D, Goldberg R, Gottlieb DJ, Hudgel D, Sateia M, Schwab R, Portable Monitoring Task Force of the American Academy of Sleep Medicine (2007) Clinical guidelines for the use of unattended portable monitors in the diagnosis of obstructive sleep apnea in adult patients. J Clin Sleep Med 3:737–747
Netzer NC, Stoohs RA, Netzer CM, Clark K, Strohl KP (1999) Using the Berlin Questionnaire to identify patients at risk for the sleep apnea syndrome. Ann Intern Med 131:485–491
Johns MW (1991) A new method for measuring daytime sleepiness: the Epworth sleepiness scale. Sleep 14:540–545
Rechtschaffen A, Kales A (1968) A manual of standardized terminology, techniques, and scoring systems for sleep stages of human subjects. Brain Information/Brain Research Institute UCLA, Los Angeles
American Academy of Sleep Medicine (1999) Sleep-related breathing disorders in adults: recommendations for syndrome definition and measurement techniques in clinical research. The report of an American Academy of Sleep Medicine Task Force. Sleep 22:667–689
No authors listed (1992) EEG arousals: scoring rules and examples: a preliminary report from the Sleep Disorders Atlas Task Force of the American Sleep Disorders Association. Sleep 15:174–182
American Sleep Disorders Association (1993) Recording and scoring leg movements—Atlas Task Force. Sleep 16:748–759
Santos-Silva R, Sartori DE, Truksinas V, Truksinas E, Alonso FF, Tufik S, Bittencourt LRA (2009) Validation of a portable monitoring system for the diagnosis of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Sleep 32:629–636
Yin M, Miyazaki S, Itasaka Y, Shibata Y, Abe T, Miyoshi A, Ishikawa K, Togawa K (2005) A preliminary study on application of portable monitoring for diagnosis of obstructive sleep apnea. Auris Nasus Larynx 32:151–156
Yin M, Miyazaki S, Ishikawa K (2006) Evaluation of type 3 portable monitoring in unattended home setting for suspected sleep apnea: factors that may affect its accuracy. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 134:204–209
White D, Gibb T, Wall J, Westbrook PR (1995) Assessment of accuracy and analysis time of a novel device to monitor sleep and breathing in the home. Sleep 18:115–126
Tonelli de Oliveira AC, Martinez D, Vasconcelos LF, Gonçalves SC, Lenz MC, Fuchs SC, Gus M, Abreu-Silva EO, Moreira LB, Fuchs FD (2009) Diagnosis of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome and its outcomes with home portable monitoring. Chest 135:330–336
To KW, Chan WC, Chan TO, Tung A, Ngai J, Ng S, Choo KL, Hui DS (2009) Validation study of a portable monitoring device for identifying OSA in a symptomatic patient population. Respirology 14:270–275
Dingli K, Coleman EL, Vennelle M, Finch SP, Wraith PK, Mackay TW, Douglas NJ (2003) Evaluation of a portable device for diagnosing the sleep apnoea/hypopnoea syndrome. Eur Respir J 21:253–259
Nigro CA, Dibur E, Malnis S, Grandval S, Nogueira F (2012) Validation of ApneaLink Ox™ for the diagnosis of obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Breath. doi:10.1007/s11325-012-0684-4
Flemons WW, Littner MR, Rowley JA, Gay P, Anderson WM, Hudgel DW, McEvoy RD, Loube DI (2003) Home diagnosis of sleep apnea: a systematic review of the literature. An evidence review cosponsored by the American Academy of Sleep Medicine, the American College of Chest Physicians, and the American Thoracic Society. Chest 124:1543–1579
Chan ED, Welsh CH (1998) Geriatric respiratory medicine. Chest 114:1704–1733
Kronenberg RS, Drage CW, Ponto RA, Williams LE (1973) The effect of age on the distribution of ventilation and perfusion in the lung. Am Rev Respir Dis 108:576–586
Peterson DD, Pack AI, Silage DA, Fishman AP (1981) Effects of aging on ventilatory and occlusion pressure responses to hypoxia and hypercapnia. Am Rev Respir Dis 124:387–391
Brischetto MJ, Millman RP, Peterson DD, Silage DA, Pack AI (1984) Effect of aging on ventilatory response to exercise and CO2. J Appl Physiol 56:1143–1150
Janssens JP, Pautex S, Hilleret H, Michel JP (2000) Sleep disordered breathing in the elderly. Aging 12:417–429
Tack M, Altose MD, Cherniack NS (1981) Effect of aging on respiratory sensations produced by elastic loads. J Appl Physiol 50:844–850
Lavie P, Lavie L (2009) Unexpected survival advantage in elderly people with moderate sleep apnoea. J Sleep Res 18:397–403
Bittencourt LR, Suchecki D, Tufik S, Peres C, Togeiro SM, Bagnato MC, Nery LE (2001) The variability of the apnoea-hypopnoea index. J Sleep Res 10:245–251
Maestri R, La Rovere MT, Robbi E, Pinna GD (2001) Night-to-night repeatability of measurements of nocturnal breathing disorders in clinically stable chronic heart failure patients. Sleep Breath 15(4):673–678
Hirshkowitz M, Moore CA, Hamilton CR 3rd, Rando KC, Karacan I (1992) Polysomnography of adults and elderly: sleep architecture, respiration, and leg movement. J Clin Neurophysiol 9:56–62
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the Associaçao Fundo de Incentivo a Pesquisa and Fundaçao de Amparo a Pesquisa do Estado de Sao Paulo (# 07/50525-1 to RS-S and CEPID no. 98/14303-3 to ST). ST and LRAB received the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq) fellowship. We would like to thank Philips, who provided the Stardust II® and training on the operation of the devices and the host software.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Polese, J.F., Santos-Silva, R., de Oliveira Ferrari, P.M. et al. Is portable monitoring for diagnosing obstructive sleep apnea syndrome suitable in elderly population?. Sleep Breath 17, 679–686 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-012-0742-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-012-0742-y