Abstract
Background
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the predictors of a 3-month mortality rate of acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) and provide a new staging system.
Methods
A total of 594 patients with IPF were included in this retrospective, observational study conducted from January 2001 to December 2010 at Okinawa Chubu Hospital.
Results
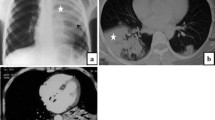
Among the 594 patients, 58 (9.8 %) developed acute exacerbation (AE) of IPF during the 10-year observation period. The median follow-up period for AE was 10.4 months. In-hospital mortality was 56.9 % and the 3-month mortality rate was 63.8 %. We identified the following four parameters in a multivariate analysis as: serum lactate dehydrogenase, sialylated carbohydrate antigen (KL-6), ratio of partial pressure of oxygen and fraction of inspiratory oxygen, and total extent of abnormal findings on high-resolution computed tomography of the chest. Patients were divided into two groups on the basis of the four composite parameters. Patients in the extensive disease-stage group required more mechanical ventilation and intensive therapy than those in the limited disease-stage group. The 3-month mortality rate was higher in patients in the extensive disease-stage group than in patients in the limited disease-stage group (80.6 vs. 54.5 %, respectively; p = 0.007).
Conclusions
Staging of AE in patients with IPF provided useful information regarding disease severity and short-term outcome.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Thoracic Society, European Respiratory Society (2000) Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: diagnosis and treatment. International consensus statement. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 161:646–664
Kim DS, Collard HR, King TE Jr (2006) Classification and natural history of the idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. Proc Am Thorac Soc 3:285–292
Ley B, Collard HR, King TE Jr (2011) Clinical course and prediction of survival in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 183:431–440
Kondoh Y, Taniguchi H, Kawabata Y, Yokoi T, Suzuki K, Takagi K (1993) Acute exacerbation in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Analysis of clinical and pathologic findings in three cases. Chest 103(6):1808–1812
Panos RJ, Mortenson RL, Niccoli SA et al (1990) Clinical deterioration in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: causes and assessment. Am J Med 88:396–404
Collard HR, Moore BB, Flaherty KR et al (2007) Acute exacerbations of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 176:636–643
Song JW, Hong S-B, Lim C-M, Koh Y, Kim DS (2011) Acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: incidence, risk factors and outcome. Eur Respir J 37:356–363
Kondoh Y, Taniguchi H, Katsuta T, Kataoka K, Kimura T, Nishiyama O, Sakamoto K, Johkoh T, Nishimura M, Ono K, Kitaichi M (2010) Risk factors of acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis 27(2):103–110
Nishimura K, Kitaichi M, Izumi T, Nagai S, Kanaoka M, Itoh H (1992) Usual interstitial pneumonia: histologic correlation with high-resolution CT. Radiology 182:337–342
Johkoh T, Muller NL, Cartier Y, Kavanagh PV, Hartman TE, Akira M, Ichikado K, Ando M, Nakamura H (1999) Idiopathic interstitial pneumonias: diagnostic accuracy of thin-section CT in 129 patients. Radiology 211:555–560
Hansell DM, Bankier AA, Macmahon H, McLoud TC, Muller NL, Remy J (2008) Fleischner society: glossary of terms for thoracic imaging. Radiology 246:697–722
Meyer KC, Raghu G, Baughman RP, Brown KK, Costabel U, du Bois RM, Drent M, Haslam PL, Kim DS, Nagai S, Rottoli P, Saltini C, Selman M, Strange C, Wood B (2012) An Official American Thoracic Society Clinical Practice Guideline: the clinical utility of bronchoalveolar lavage cellular analysis in interstitial lung disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 185:1004–1014
Bestall JC, Paul EA, Garrod R, Garnham R, Jones PW, Wedzicha JA (1999) Usefulness of the Medical Research Council (MRC) dyspnoea scale as a measure of disability in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Thorax 54:581–586
Akira M, Hamada H, Sakatani M, Kobayashi C, Nishioka M, Yamamoto S (1997) CT findings during phase of accelerated deterioration in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Roentgenol 168:79–83
Kim DS, Park JH, Park BK, Lee JS, Nicholson AG, Colby T (2006) Acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: frequency and clinical features. Eur Respir J 27:143–150
Akira M, Sakatani M, Ueda E (1993) Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: progression of honeycombing at thin-section CT. Radiology 189:687–691
Sumikawa H, Johkoh T, Colby TV, Ichikado K, Suga M, Taniguchi H, Kondoh Y, Ogura T, Arakawa H, Fujimoto K, Inoue A, Mihara N, Honda O, Tomiyama N, Nakamura H, Mu¨ller ML (2008) Computed tomography findings in pathological usual interstitial pneumonia. Relationship to survival. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 177:433–439
Nagai S, Kitaichi M, Hamada Knagao T, Hoshino Y, Miki H, Izumi T (1999) Hospital-based historical cohort study of 234 histologically proven Japanese patients with IPF. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis 16:209–214
Stern J-B, Mal H, Groussard O, Brugière O, Marceau A, Jebrak G, Fournier M (2001) Prognosis of patients with advanced idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis requiring mechanical ventilation for acute respiratory failure. Chest 120(1):213–219
Fernandez-Perez ER, Yilmaz M, Jenad H, Daniels CE, Ryu JH, Hubmayr RD, Gajic O (2008) Ventilator settings and outcome of respiratory failure in chronic interstitial lung disease. Chest 133(5):1113–1119
Saydain G, Islam A, Afessa B, Ryu JH, Scott JP, Peters SG (2002) Outcome of patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis admitted to the intensive care unit. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 166:839–842
Wells AU, Desai SR, Rubens MB, Goh NS, Cramer D, Nicholson AG, Colby TV, du Bois RM, Hansell DM (2003) Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a composite physiologic index derived from disease extent observed by computed tomography. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 167(7):962–969
du Bois RM, Weycker D, Albera C, Bradford WZ, Costabel U, Kartashov A, King TE Jr, Lancaster L, Noble PW, Sahn SA, Thomeer M, Valeyre D, Wells AU (2011) Forced vital capacity in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Test properties and minimal clinically important difference. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 184:1382–1389
Akira M, Kozuka T, Yamamoto S, Sakatani M (2008) Computed tomography findings in acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 178:372–378
Kondoh Y, Taniguchi H, Yokoi T, Nishiyama O, Ohishi T, Kato T, Suzuki K, Suzuki R (2005) Cyclophosphamide and low-dose prednisolone in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and fibrosing nonspecific interstitial pneumonia. Eur Respir J 25:528–533
Parambil JG, Myers JL, Ryu JH (2005) Histopathologic features and outcome of patients with acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis undergoing surgical lung biopsy. Chest 128:3310–3315
Kondo A, Saiki S (1989) Acute exacerbation in idiopathic interstitial pneumonia (IIP). In: Harasawa M, Fukuchi Y, Morinari H (eds) Interstitial pneumonia of unknown etiology. University of Tokyo Press, Tokyo, pp 33–42
Homma S, Sakamoto S, Kawabata M, Kishi K, Tsuboi E, Motoi N, Yoshimura K (2005) Cyclosporin treatment in steroid-resistant and acutely exacerbated interstitial pneumonia. Intern Med 44:1144–1150
Pereira CAC, Malheiros T, Coletta EM, Ferreira RG, Rubin AS, Otta JS, Rocha NS (2006) Survival in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis cytotoxic agents compared to corticosteroids. Respir Med 100:340–347
Acknowledgments
The authors thank all of our residents and Drs. Yasutani and Takara for their interpretation of the medical records and imaging results.
Conflict of interest
All the authors declare none.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kishaba, T., Tamaki, H., Shimaoka, Y. et al. Staging of Acute Exacerbation in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Lung 192, 141–149 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00408-013-9530-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00408-013-9530-0