Abstract
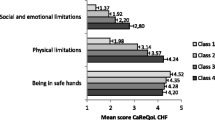
The authors developed a new measure of subjective health status for patients with heart failure. Eighty-eight patients with heart failure were asked about the impact of their condition on 123 items related to physical and emotional function. The most frequently chosen and important items were included in a 16-item Chronic Heart Failure Questionnaire (CHQ) that examines dyspnea during daily activities, fatigue, and emotional function. The CHQ was tested in a controlled trial of digoxin in heart failure patients in sinus rhythm. When administered serially to 25 patients in the run-in phase of the trial, the CHQ proved reproducible. Subsequently, CHQ results distinguished those who reported improvement or deterioration from those who did not. The CHQ showed moderate correlations with patient global ratings, walk test scores, and clinical assessments of heart failure. The authors conclude that the CHQ may be useful for measuring health status in clinical trials in heart failure.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
The Consensus Trial Study Group. Effects of enalapril on mortality in severe congestive heart failure. N Engl J Med. 1987;316:1429–35.
Cohn JN, Archibald DG, Ziesche S, et al. Effect of vasodilator therapy on mortality in chronic congestive heart failure: results of a Veterans Administration Cooperative Study. N Engl J Med. 1986;314:1547–52.
Guyatt GH. Methodologic problems in clinical trials in heart failure. J Chronic Dis. 1985;38:353–63.
Guyatt GH, Thompson PJ, Berman LB, et al. How should we measure function in patients with chronic heart and lung disease? J Chronic Dis. 1985;38:517–24.
Goldman L, Hashimoto D, Cook EF. Comparative reproducibility and validity of systems for assessing cardiovascular functional class: advantages of a new specific activity Scale. Circulation. 1981;64:1227–34.
Captopril Multicenter Research Group. A placebo-controlled trial of captopril in refractory chronic congestive heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1983;2:755–63.
Massie B, Bourassa M, DiBianco R, et al. Long-term oral administration of amrinone for congestive heart failure: lack of efficacy in a multicenter controlled trial. Circulation. 1985;71:963–71.
DiBianco R, Shabetai R, Silverman BD, Leier CV, Benotti JR, and The Amrinone Multicenter Study Investigators. Oral amrinone for the treatment of chronic congestive heart failure: results of a multicenter randomized double-blind and placebo-controlled withdrawal study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1984;4:855–66.
Sharpe DN, Murphy J, Coxon R, Hannan SF. Enalapril in patients with chronic heart failure: a placebo-controlled, randomized, double-blind study. Circulation. 1984;70:271–8.
Kirshner B, Guyatt GH. A methodologic framework for assessing health indices. J Chronic Dis. 1985;38:27–36.
Guyatt GH, Bombardier C, Tugwell PX. Measuring disease-specific quality of life in clinical trials. Canad Med Assoc J. 1986;134:889–95.
Brook RH, Ware JE, Davies-Avery A, et al. Overview of validity and the index of well-being. Health Serv Res. 1976;11:478–507.
Bergner M, Bobbitt RA, Carter WB, Gilson BS. The sickness impact profile: development and final revision of a health status measure. Med Care 1981;19:787–805.
Guyatt GH, Townsend M, Berman LB, Pugsley SO. Quality of life in patients with chronic airflow limitation. Br J Dis Chest 1987;81:45–54.
Guyatt GH, Sullivan MJJ, Fallen EL, et al. A controlled trial of digoxin in heart failure. Am J Cardiol. 1988;61:371–5.
Lee DC, Johnson RA, Bingham JB, et al. Heart failure in outpatients: a randomized trial of digoxin versus placebo. N Engl J Med. 1982;306:699–705.
Guyatt GH, Sullivan MJ, Fallen EL, Pugsley SO, Taylor DW, Berman LB. The six minute walk: a new measure of exercise capacity in patients with chronic heart failure. Canad Med Assoc J. 1985;132:919–23.
Guyatt GH, Walter S, Norman G. Measuring change over time: assessing the usefulness of evaluative instruments. J Chronic Dis. 1987;40:171–8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received from the Department of Clinical Epidemiology and Biostatistics and the Department of Medicine, McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario, Canada.
Presented in part at the 1984 meeting of the Association of American Physicians.
Supported by the Ontario Ministry of Health. Dr. Guyatt is a Career Scientist of the Ontario Ministry of Health.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guyatt, G.H., Nogradi, S., Halcrow, S. et al. Development and testing of a new measure of health status for clinical trials in heart failure. J Gen Intern Med 4, 101–107 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02602348
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02602348