Abstract
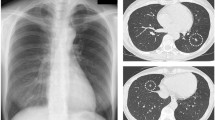
Hypercalcaemia and hypercalciuria were diagnosed in a 21-week-old boy with miliary tuberculosis. The tuberculosis was treated with isoniazid, rifampin and streptomycin. After 2 months, streptomycin was replaced by ethambutol. The hypercalcaemia was treated initially with prednisone, which decreased the serum 1,25 (OH)2 cholecalciferol level but the serum calcium level remained unaltered. After calcium and vitamin D restriction, the serum calcium level normalized within 1 day. The patient's tuberculosis was treated and he remains well.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bell NH, Shary J, Shaw S, Turner R (1985) Hypercalcemia associated with increased circulating 1,25 dihydroxyvitamin D in a patient with pulmonary tuberculosis. Calcif Tissue Int 37:588–591
Coe F (1984) Treatment of hypercalciuria. N Engl J Med 311:116–117
Fox J, Ross R, Care AD (1985) Effects of acute and chronic treatment with glucocorticoids on the intestinal absorption of calcium and phosphate and on plasma 1,25 dihydroxyvitamin D levels in pigs. Clin Sci 69:553–559
Gkonos PJ, London R, Hendler ED (1984) Hypercalcemia and elevated 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D levels in a patient with end stage renal disease and active tuberculosis. N Engl J Med 311:1683–1685
Isaacs RD, Nicholson GI, Holdaway IM (1987) Miliary tuberculosis with hypercalcaemia and raised vitamin D concentrations. Thorax 42:555–556
Johnson NM, Shneerson G (1980) Hypercalcaemia and hypercalciuria associated with pulmonary tuberculosis. Br J Dis Chest 74: 201–202
Kitrou MP, Phytou Pallikari A, Tzannes SE, Virvidakis K, Mountokalakis T (1983) Serum calcium during chemotherapy for active tuberculosis. Eur J Respir Dis 64:347–354
Kruse K (1987) Endocrine control and disturbances of calcium and phosphate metabolism in children. Eur J Pediatr 1987:146: 346–353
Shai L, Baker RK, Addrizo JR, Wallach T (1972) Hypercalcemia in Mycobacterial infection. J Clin Endocrinol 34:251–256
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gerritsen, J., Knol, K. Hypercalcaemia in a child with miliary tuberculosis. Eur J Pediatr 148, 650–651 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00441524
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00441524